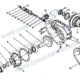
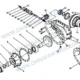
Différentiel de roue russe FAW: Déconstruction 35 Composants pour la stabilité du couple arctique
Le Différentiel de roue russe FAW assembly is the kinetic anchor of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck. Designed specifically for the Siberian mining sector, this system manages torque distribution across the middle axle on ice-covered gradients. It integrates impact-resistant metallurgy with precise pneumatic locking logic. Ce guide analyse les Différentiel de roue russe FAW breakdown to ensure fleet uptime in -50°C environments.

Différentiel de roue russe FAW
Gear Geometry and Kinetic Transfer
La fonction essentielle du Différentiel de roue russe FAW is to translate rotational energy into forward motion while allowing for cornering speed variances. This is achieved through the interaction between the Active Bevel Gear (Partie no. 2502036BA6E) and the Driven Cylindrical Gear (Partie no. 2502108-A6E). Dans le Différentiel de roue russe FAW configuration, these gears are ground to a specialized profile that increases the contact patch area. This design modification is critical for distributing the shock loads encountered when a loaded truck transitions from slippery ice to dry rock, preventing tooth fracture.
Maintaining the precise alignment of these gears is the Adjusting Washer – Roulement à engrenages coniques actifs (Partie no. 2402081-A0E). This component allows technicians to set the pinion depth of the Différentiel de roue russe FAW with extreme accuracy. If the depth is incorrect, the mesh point shifts to the weaker tip of the gear tooth, conduisant à un échec catastrophique. The use of these washers enables the Différentiel de roue russe FAW to be rebuilt indefinitely, as wear can be compensated for during overhaul procedures.
The rotational stability of the Différentiel de roue russe FAW is supported by the Tapered Roller Bearing (Partie no. 32314) and the larger Tapered Roller Bearing (Partie no. 32315). These bearings are arranged to handle the massive axial thrust generated by the spiral bevel design. Separating them is the Spacer – Roulement à engrenages coniques actifs (Partie no. 2502088-A0E). This spacer is machined from a steel alloy with a thermal expansion coefficient identical to the housing, ensuring that the bearing preload within the Différentiel de roue russe FAW remains constant across the extreme temperature fluctuations of the Russian Arctic.
En outre, the Bearing Seat (Partie no. 2502049-A6E) acts as the rigid foundation for the input shaft. It is secured to the main housing with a calculated clamping force. The interface uses the Adjusting Shim – Siège de roulement à engrenage conique actif (Partie no. 2502097-A6E) to fine-tune the backlash. This adjustability is a hallmark of the Différentiel de roue russe FAW conception, allowing maintenance teams to optimize the gear mesh for silence and longevity, even after thousands of hours of severe duty operation.
Pneumatic Traction Control System
The defining characteristic of the Différentiel de roue russe FAW in off-road scenarios is its inter-wheel locking mechanism. This system is powered by the Cylinder – Wheel Differential Lock (Partie no. 2406011-A0E). When the driver engages the lock, compressed air forces the Piston – Wheel Differential Lock (Partie no. 2406013-A0E) to extend. This action must be instantaneous to prevent the vehicle from losing momentum. Le Différentiel de roue russe FAW relies on this rapid engagement to synchronize the wheel speeds before the truck becomes hopelessly boggged down.
Crucial to this operation is the sealing integrity provided by the O-ring – Piston de blocage de différentiel (Partie no. 2406014-55R.). Unlike standard seals, this component uses a low-temperature elastomer formulation. Dans le contexte du Différentiel de roue russe FAW, this material science is vital; standard rubber would shatter at -50°C, causing an air leak. A leaking seal would render the lock inoperable, highlighting why genuine parts are essential for the Différentiel de roue russe FAW to function in its intended environment.
The mechanical link is established by the Shift Fork – Wheel Differential Lock (Partie no. 2406024-A0E), which slides the Moving Sleeve – Wheel Differential Lock (Partie no. 2406032-A0E) into the Fixed Sleeve – Wheel Differential Lock (Partie no. 2406033-A0E). The splines on these sleeves are heat-treated to resist rounding. La précision du Différentiel de roue russe FAW shift mechanism ensures that the sleeve engages fully every time, empêcher le “skipping” that damages splines and contaminates the oil with metal shavings.
Disengagement is handled by the Return Spring – Wheel Differential Lock (Partie no. 2406028-A0E). This spring must be strong enough to overcome the friction of the cold lubricant to retract the piston. Si le Différentiel de roue russe FAW fails to unlock on high-traction surfaces, the axle shafts will bind during turns, leading to breakage. Donc, the spring tension is a critical safety parameter within the Différentiel de roue russe FAW assemblée, monitored by the Wheel Differential Lock Switch Assembly (Partie no. 3834050-A0E).
Housing Durability and Maintenance
The structural backbone of the assembly is the Reducer Shell (Partie no. 2502015-A6E). This casting encapsulates the entire Différentiel de roue russe FAW gear set. It is manufactured from nodular cast iron chosen for its ductility at low temperatures. While standard iron becomes brittle and prone to cracking in the Arctic, le Différentiel de roue russe FAW shell is engineered to flex microscopically under impact loads, preserving the alignment of the internal components and preventing catastrophic housing rupture.
To secure this heavy assembly to the axle, high-strength fasteners are employed. Le boulon – Réducteur de fixation (Partie no. 2402016-1H) is a flange bolt designed to maintain high clamping loads. Dans le Différentiel de roue russe FAW application, these bolts are torqued to specific yield points. This ensures that the reducer shell does not shift relative to the axle housing, a movement that would misalign the driveshaft. L'intégrité du Différentiel de roue russe FAW depends on these bolts maintaining tension under severe vibration.
Reaction forces are managed by the Supporting Pin – Coque réductrice & Boîtier d'essieu (Partie no. 2402021-A0E). These pins act as shear anchors, absorbing the torsional load generated when the Différentiel de roue russe FAW transmits torque to the wheels. By offloading the shear stress from the mounting bolts, these pins significantly extend the service life of the fasteners. This redundancy is a key safety feature of the Différentiel de roue russe FAW design philosophy.
Enfin, preventative maintenance is facilitated by the Hexagon Cone Magnetic Plug (Partie no. T62106). This plug captures ferrous debris generated by normal wear within the Différentiel de roue russe FAW. Regular inspection of this plug provides early warning of abnormal gear or bearing degradation. By monitoring the debris accumulation, fleet managers can schedule proactive repairs, Assurer le Différentiel de roue russe FAW delivers reliable performance throughout the harsh winter season.
Répartition des composants: 137. Coque réductrice, Engrenage conique actif, Wheel Differential
| Non. |
Numéro de pièce |
Nom de la pièce |
Quantité |
| – | 2502010-55R. | Ensemble réducteur principal de l'essieu central (je=1.500) | 1 |
| 1 | 2402069-A0E | Noix – Bride d'engrenage conique actif | 1 |
| 2 | 2502108-A6E | Engrenage cylindrique entraîné | 1 |
| 3 | 32314 | Roulement à rouleaux coniques | 1 |
| 4 | 2402081-A0E | Rondelle de réglage – Roulement à engrenages coniques actifs | 1 |
| 5 | 2502088-A0E | Entretoise – Roulement à engrenages coniques actifs | 1 |
| 6 | 2402016-1H | Boulon – Réducteur de fixation | 12 |
| 7 | 2502049-A6E | Siège de roulement | 1 |
| 8 | 2502097-A6E | Réglage de la cale – Siège de roulement à engrenage conique actif | Comme demande |
| 9 | 2402048-A0E | Bouclier d'huile – Siège de roulement à engrenage conique actif | 1 |
| 10 | 32315 | Roulement à rouleaux coniques | 1 |
| 11 | 2502036BA6E | Engrenage conique actif | 1 |
| 12 | T62106 | Bouchon magnétique à cône hexagonal | 1 |
| 13 | 2402017-1H | Boulon – Réducteur de fixation | 18 |
| 14 | 2403071-A0E | Bague de réglage – Roulement différentiel | 2 |
| 15 | 2503010BA6E | Assemblage différentiel | 1 |
| 16 | 2403072-A0E | Plaque de verrouillage – Bague de réglage | 2 |
| 17 | CQ1500812S | Boulon pilote à tête hexagonale | 2 |
| 18 | 2402023-A0E | Boulon – Fixation du chapeau de palier de différentiel | 4 |
| 19 | 2402021-A0E | Goupille de support – Coque réductrice & Boîtier d'essieu | 2 |
| 20 | 2406034-A0E | Anneau de retenue en fil d'acier – Manchon fixe de blocage de différentiel | 1 |
| 21 | 2406033-A0E | Manchon fixe – Wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 22 | 2406032-A0E | Manchon mobile – Wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 23 | 2402016-A0E | Boulon – Réducteur de fixation | 2 |
| 24 | 2406028-A0E | Retour printemps – Wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 25 | 2406024-A0E | Fourche de changement de vitesse – Wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 26 | 2406025-A0E | Ensemble d'arbre de fourche de changement de vitesse | 1 |
| 27 | 2406014-55R. | Joint torique – Piston de blocage de différentiel | 1 |
| 28 | 2406013-A0E | Piston – Wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 29 | 2406011-A0E | Cylindre – Wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 30 | 2406017-A0E | Joint – Couvercle de cylindre | 1 |
| 31 | 2406016-A0E | Couverture – Cylindre | 1 |
| 32 | 2406018-A0E | Boulon – Fastening Wheel Diff Lock Cylinder Cover | 3 |
| 33 | CQ63505 | Raccord coudé – Joint de tuyau conique | 1 |
| 34 | 3834050-A0E | Wheel Differential Lock Switch Assembly | 1 |
| 35 | 2502015-A6E | Coque réductrice & Ensemble de chapeau de roulement de différentiel | 1 |
| 35-1 | 2502018-A6E | Coque réductrice – Essieu central | 1 |
| 35-2 | 2402019-A0E | Capuchon – Roulement différentiel | 1 |
| 35-3 | 2502019-A0E | Capuchon – Roulement différentiel | 1 |
Conclusion: The Arctic Operational Standard
Le Différentiel de roue russe FAW is more than a simple gear assembly; it is a strategic asset for operations in the High North. Chaque composant, from the low-temperature O-rings to the impact-resistant reducer shell, has been selected to provide maximum reliability when the thermometer drops below -40°C. Pour les gestionnaires de flotte, understanding the intricacies of the Différentiel de roue russe FAW—specifically the pneumatic locking mechanism and the bearing preload requirements—is the key to reducing unscheduled downtime and maintaining logistical flow.
By adhering to the maintenance protocols outlined in this breakdown, and utilizing only genuine FAW parts for the Différentiel de roue russe FAW, operators can ensure that their CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump trucks remain operational throughout the harsh Siberian winter. The integration of robust mechanical design with precise pneumatic control allows the Différentiel de roue russe FAW to deliver unparalleled traction, proving that with the right engineering, no terrain is impassable.
Emballage et logistique
Pièces FAW, y compris l'ensemble bloc-cylindres, sont emballés avec soin pour garantir une livraison en toute sécurité. Chaque composant est sécurisé dans des matériaux de protection pour éviter tout dommage pendant le transport. Le réseau logistique garantit des expéditions ponctuelles dans le monde entier, soutenir des opérations de maintenance efficaces. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une image illustrant l'emballage standard des pièces de camion FAW., mettant en valeur l’attention portée aux détails dans la manipulation et le stockage.
Cette approche d'emballage minimise le risque de corrosion ou de dommages causés par les chocs., s'assurer que les pièces comme l'ensemble bloc-cylindres FAW arrivent en parfait état. Les clients peuvent compter sur la logistique de FAW pour une qualité et une fiabilité constantes.