Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW: Maîtriser 12 Composants stratégiques pour un contrôle inflexible de la transmission
Le Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW is the hydraulic and pneumatic nerve center of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck’s driveline. Bridging the gap between the driver’s pedal and the transmission housing, this assembly translates human effort into massive mechanical leverage. Designed for the frozen expanse of the Russian Federation, it ensures smooth, fatigue-free shifting even when hydraulic fluids thicken in -40°C conditions. Ce guide décortique le 12 essential components defining this system.
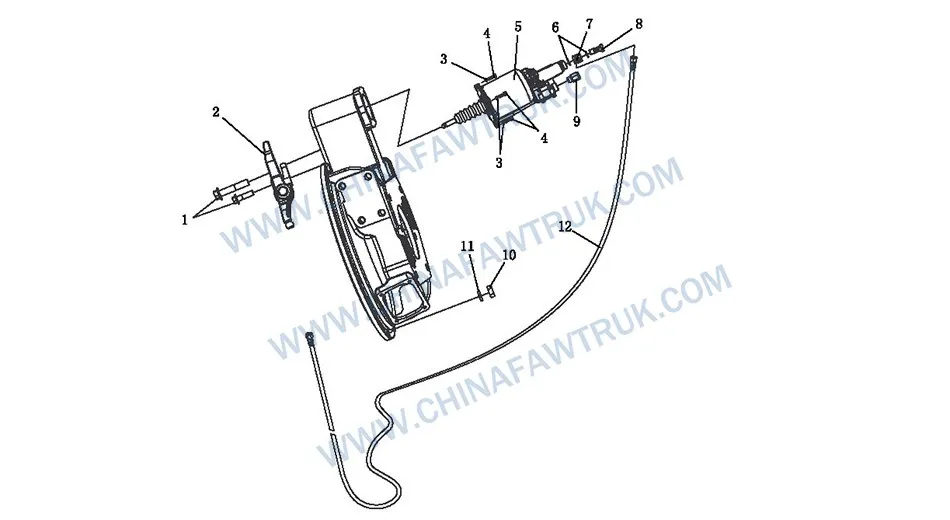
FAW Russian Clutch Control Mechanism Logic Assembly
Dynamique d'actionnement: The Clutch Booster Pump
Au coeur du Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW ment le Ensemble de pompe de surpression d'embrayage (Partie no. 1602305A70A). In the context of heavy-duty trucks, manual actuation of the clutch pressure plate requires immense force, far beyond what a driver can comfortably sustain over a long shift. The booster pump utilizes compressed air from the vehicle’s pneumatic system to amplify the hydraulic pressure generated by the master cylinder. Ce “servo-assist” reduces pedal effort by up to 70%, a critical factor for driver safety and alertness on treacherous Russian mining roads.
The engineering specific to the Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW focuses on the booster’s internal seals. Par grand froid, standard rubber seals harden and shrink, leading to air leaks or hydraulic fluid bypass. If the pneumatic side leaks, the driver loses power assist, making the pedal incredibly heavy. If the hydraulic side leaks, the clutch fails to disengage entirely. FAW utilizes low-temperature nitrile or polyurethane seals designed to maintain flexibility at -40°C, ensuring consistent boost pressure and immediate response.
En outre, the housing of the booster is cast from corrosion-resistant alloy to withstand the external attack of road salts and internal moisture accumulation. The pushrod mechanism within the Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW booster is precision-machined to prevent binding. Any friction here would result in a “sticky” pedal or incomplete clutch engagement, leading to rapid wear of the friction disc. This component represents the intersection of pneumatic power and hydraulic precision.
Mechanical Logic: The Release Fork Assembly
Translating the linear motion of the booster into the rotational movement required to disengage the clutch is the job of the Release Fork and Bracket Assembly (Partie no. 1602420-896). Au sein du Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW, this component acts as a heavy-duty lever. It pivots on a fulcrum to push the release bearing against the diaphragm spring. The structural integrity of this fork is paramount; any flexing or bending under load results in lost travel, meaning the clutch may drag even when the pedal is fully depressed.
Le Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW specifies a fork forged from high-tensile steel to resist fatigue. In the stop-and-go cycle of a dump truck, this fork undergoes millions of stress cycles. The pivot points are hardened to resist wear. If the pivot wears down, the geometry of the leverage changes, altering the engagement point of the pedal. In the harsh Russian environment, where grit and dust are omnipresent, the sealing of the bell housing around this fork is essential to prevent abrasive wear on the pivot bushings.
The bracket assembly that secures the fork must be rigid. It is fastened with specific hardware to the transmission casing. Any looseness in the bracket translates to vibration and noise in the Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW. The design ensures that the fork remains perfectly aligned with the release bearing, preventing off-axis loading that could cause the bearing to seize or the fork tips to snap, a failure that would instantly immobilize the vehicle.
Fluid Logic: Tuyaux, Boulons creux, and Washers
The hydraulic pressure is delivered via the Oil Pipe Assembly – Embrayage (Partie no. 1602200-75U). Dans le Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW, this is not a standard rubber hose. It is a high-pressure reinforced line designed to minimize volumetric expansion. If the hose expands under pressure (ballooning), hydraulic force is lost, resulting in a spongy pedal feel and incomplete clutch release. The material is also formulated to resist the extreme cold, preventing cracking or stiffening that could transmit chassis vibration to the hard lines.
The connection points utilize a smart space-saving solution: le Boulon creux (Partie no. 1602243-93C), often called a banjo bolt, paired with the Transition Joint – Oil Pipe (Partie no. 1602244-93C). This configuration allows the hydraulic line to exit the booster at a 90-degree angle, essential in the crowded chassis of the J6P. The hollow bolt must be torqued precisely to compress the Laveuse de scellage (Partie no. 1602242A70A) without shearing the bolt head.
The sealing washers in the Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW are typically copper or aluminum crush washers. They are single-use items. Once compressed, they work-harden and form a perfect seal against the banjo fitting. Reusing these washers is a primary cause of hydraulic leaks. A leak in the clutch system introduces air, which is compressible, unlike fluid. Ce “air lock” renders the clutch inoperable. Donc, the integrity of these small sealing components is critical to the functionality of the entire Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW.
Dynamique de fixation: Flange Bolts and Vibration Control
Securing the components of the Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW requires robust hardware. The system utilizes Boulon à bride à tête hexagonale (Partie no. Q1851690T) et Boulon à tête hexagonale (Partie no. CQ1500825). The flange bolt is particularly important for mounting the booster pump. The integrated flange distributes the clamping load over a wider area of the aluminum booster housing, preventing cracking or deformation that could occur with a standard bolt head.
To combat the intense vibration of the diesel powertrain, the assembly relies on a multitude of locking fasteners: Écrou hexagonal (Partie no. CQ34010) et Rondelle à ressort (Partie no. Q40310). Il y a 12 of each in the assembly, highlighting the extensive mounting points required to keep the lines and brackets secure. The spring washer acts as a dynamic tensioner, maintaining load on the nut even as thermal expansion and contraction occur.
Dans le Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW logique, every fastener is a critical failure point. If a bracket bolt loosens, the rigid hydraulic lines can vibrate until they fatigue and snap. If the booster mounting bolts loosen, the pushrod alignment shifts, causing binding. Donc, la spécification de haute qualité, corrosion-resistant fasteners (likely Zinc-plated or Phosphate-coated) is essential for the long-term reliability of the system in the salty, wet conditions of Russian roads.
Répartition des composants: 101. Clutch Control Mechanism
| Non. |
Numéro de pièce |
Nom de la pièce |
Quantité |
| 1 |
Q1851690T |
Boulon à bride à tête hexagonale |
2 |
| 2 |
1602420-896 |
Release Fork and Bracket Assembly |
1 |
| 3 |
Q40308 |
Rondelle à ressort |
4 |
| 4 |
CQ1500825 |
Boulon à tête hexagonale |
4 |
| 5 |
1602305A70A |
Ensemble de pompe de surpression d'embrayage |
1 |
| 6 |
1602242A70A |
Laveuse de scellage |
2 |
| 7 |
1602244-93C |
Transition Joint – Oil Pipe |
1 |
| 8 |
1602243-93C |
Boulon creux |
1 |
| 9 |
3533055-55UN |
Straight Pipe Joint Assembly – Two-way Valve |
1 |
| 10 |
CQ34010 |
Écrou hexagonal |
12 |
| 11 | Q40310 |
Rondelle à ressort |
12 |
| 12 |
1602200-75U |
Oil Pipe Assembly – Embrayage |
1 |
Conclusion: The Seamless Interface
Le Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW is the unsung hero of vehicle drivability. It is the interface that allows the driver to command the massive torque of the engine with precision and ease. By effectively amplifying manual force and ensuring robust hydraulic integrity, this system transforms the grueling task of shifting gears in a heavy truck into a manageable process, even in the dead of winter.
Pour les exploitants de flotte, the maintenance of this system is critical for driver retention and vehicle longevity. A failing booster or a leaking pipe not only deadlines the truck but can also lead to premature clutch failure due to incomplete engagement. En investissant dans l'authentique Mécanisme de commande d'embrayage russe FAW components—specifically the cold-weather booster and reinforced piping—operators ensure that their fleet remains responsive, fiable, and ready for the toughest jobs.
Emballage et logistique
Pièces FAW, y compris l'ensemble bloc-cylindres, sont emballés avec soin pour garantir une livraison en toute sécurité. Chaque composant est sécurisé dans des matériaux de protection pour éviter tout dommage pendant le transport. Le réseau logistique garantit des expéditions ponctuelles dans le monde entier, soutenir des opérations de maintenance efficaces. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une image illustrant l'emballage standard des pièces de camion FAW., mettant en valeur l’attention portée aux détails dans la manipulation et le stockage.
Cette approche d'emballage minimise le risque de corrosion ou de dommages causés par les chocs., s'assurer que les pièces comme l'ensemble bloc-cylindres FAW arrivent en parfait état. Les clients peuvent compter sur la logistique de FAW pour une qualité et une fiabilité constantes.


