FAW Russian Brackets And Piping: 30 Strategic Components for Structural & Fluid Integrity in the Arctic
The FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly forms the skeletal and circulatory framework for the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck’s emission control system. Operating in the unforgiving Russian climate requires more than just functional components; it demands a mounting architecture capable of resisting chassis torsion on frozen mine roads and a piping network that actively combats fluid crystallization at -40°C. This guide analyzes the heated transport lines, the heavy-duty vibration isolation brackets, and the specialized fastening logic that holds the SCR system together.
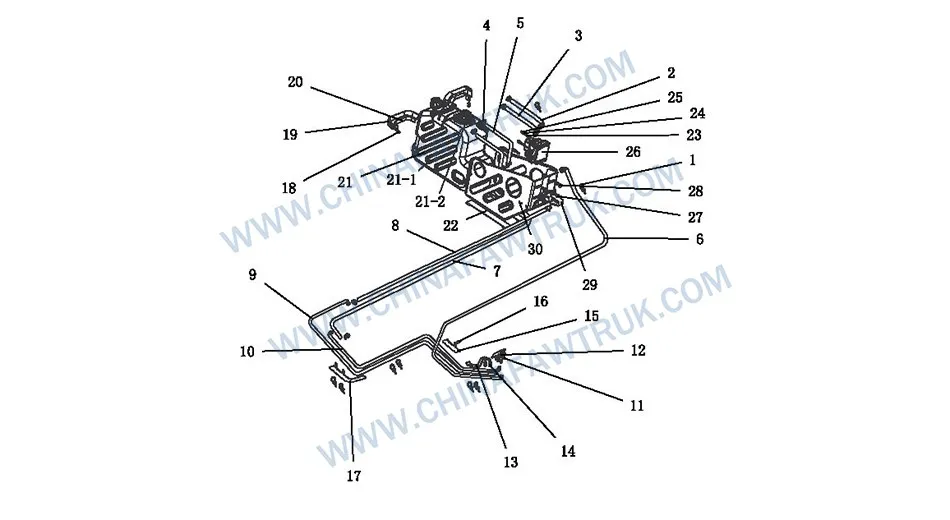
FAW Russian Brackets And Piping
Heated Transport: Fighting the Freeze
The defining feature of the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly is its sophisticated fluid transport network. In standard climates, simple rubber hoses suffice. However, in the Russian Federation, the urea solution (AdBlue) used for emissions control freezes solid at -11°C. To maintain compliance and engine performance, FAW employs a network of electrically heated lines. The Electrically Heated Urea Supply Pipe – Tank to Pump (Part No. 1160120-66W) and Electrically Heated Urea Supply Pipe – Pump to Nozzle (Part No. 1160130-66W) feature integrated resistive heating elements. These elements are wrapped around the core tube and insulated with a thermal jacket, ensuring that the fluid remains liquid from the reservoir to the injector tip, even when ambient temperatures plummet.
Complementing the electrical heating is a coolant-based thermal management loop. The Urea Heating Inlet Water Pipe – Engine to Solenoid (Part No. 1160128-55R) and Urea Heating Return Water Pipe (Part No. 1160127-28V) circulate hot engine coolant to the urea tank coil. This bulk heating capability is critical for thawing the main reservoir after a long overnight park. The piping materials used in the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping system are formulated from high-grade EPDM and reinforced polymers to withstand the dual stresses of internal chemical corrosion from urea and external thermal shock from the Arctic environment.
The system also includes specialized cooling lines for the injector itself, specifically the Urea Nozzle Cooling Inlet Water Pipe Assembly (Part No. 1160315-61S). While heating is needed for the fluid, the nozzle tip sits in the exhaust stream and requires active cooling to prevent the solenoid from overheating. This duality—heating the lines while cooling the nozzle—demonstrates the complex thermal balancing act performed by the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping system. Each pipe is precision-bent to route through the chassis without rubbing against sharp edges or hot exhaust components, a critical layout consideration for longevity.
Connections are secured with the Small Worm Drive Hose Clamp (Part No. CQ67625). Unlike spring clamps which can lose tension in extreme cold due to metal fatigue, worm drive clamps allow for positive mechanical torque application. This ensures that the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping connections remain leak-free even as the hoses contract slightly in sub-zero temperatures.
Structural Rigidity: The Bracket Architecture
The plumbing network is supported by a series of heavy-duty brackets designed to isolate the lines from chassis vibration. The Urea Nozzle Piping Bracket (Part No. 1160126-73W) and Urea Pump Piping Bracket (Part No. 1160126-61S) act as the primary anchor points. In the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly, these brackets are manufactured from thick-gauge steel, often stamped with stiffening ribs to raise their natural frequency. This prevents the brackets from resonating with the diesel engine’s vibration, which would otherwise lead to fatigue cracks and eventual failure.
The largest structural component is the Urea Tank Bracket Welding Assembly (Part No. 1160105-66W). This welded assembly must support the full weight of the urea tank (approximately 40-50kg when full) while the truck navigates the rough, frozen terrain of a Siberian mine. The bracket design utilizes a cantilevered geometry that transfers load directly to the frame rails. The FAW Russian Brackets And Piping engineering standards dictate high-quality welds and corrosion-resistant coatings (such as powder coating or hot-dip galvanizing) to prevent rust jacking in the salt-laden winter road environment.
To secure the tank to the bracket, the system uses the Urea Tank Strap Assembly (Part No. 1160140-66W). These stainless steel straps provide high tensile strength. However, metal-on-plastic contact is avoided by using the Strap Liner (Part No. 1160134-87V). This rubber interface is a critical part of the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping system. It provides friction to hold the tank in place and acts as a damper to absorb high-frequency vibrations that could otherwise abrade the polymer tank wall, leading to leaks.
Additional support is provided by the Urea Piping Bracket (Part No. 1160126A76R) and the secondary Urea Nozzle Piping Bracket (Part No. 1160126-93B). These smaller brackets manage the routing of the flexible lines, ensuring they maintain proper bend radii and do not droop onto the driveshaft or exhaust. The meticulous placement of these supports highlights the attention to detail in the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping layout.
Secure Fixation: Bolts, Nuts, and Cable Ties
The integrity of the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly relies on a specific suite of fasteners. The Hexagon Flange Bolt (Standard) (Part No. Q1841445T) and the Hex Head Convex Bolt (Part No. Q1841455T) are the primary structural fasteners. The flange head design is essential for distributing clamping load over the bracket surfaces, preventing the bolt head from embedding into the metal and losing torque.
For mounting smaller components, the Combination Bolt (Part Nos. CQ1460816 and CQ1461025) is utilized. These bolts feature integrated captive washers, which speed up assembly and ensure that a washer is never forgotten during maintenance. In the high-vibration environment of the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping system, maintaining bolt preload is vital. A loose bracket can cause a domino effect of failures, leading to ruptured lines and emissions system shutdown.
Cable management is handled by the Plastic Cable Tie (Part No. T67417246). There are 24 of these units specified in the breakdown. These are not standard nylon ties; they are formulated with impact modifiers to remain flexible at -40°C. Standard ties would shatter in the Russian cold, leaving wiring and hoses unsupported. The FAW Russian Brackets And Piping system relies on these ties to bundle hoses together, increasing their collective stiffness and resistance to harmonic vibration.
Finally, the connection of the nozzle assembly uses the Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw (Part No. CQ2180625). This high-strength fastener allows for precise torque application in the confined space near the exhaust pipe. The use of high-grade steel for these screws ensures they do not stretch or yield under the thermal expansion cycles of the exhaust system, maintaining a gas-tight seal for the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping interface.
Component Breakdown List
The following table provides the complete, unedited breakdown of the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly. It includes all 30 component types listed in the assembly diagrams, ensuring that every bracket, pipe, and fastener is accounted for.
| No. |
Part Number |
Part Name |
Qty |
| 1 |
T67417246 |
Plastic Cable Tie |
24 |
| 2 |
1160120-66W |
Electrically Heated Urea Supply Pipe – Tank to Pump |
1 |
| 3 |
1160250-66W |
Electrically Heated Urea Supply Pipe – Pump to Tank |
1 |
| 4 |
CQ67625 |
Small Worm Drive Hose Clamp |
6 |
| 5 |
1160129-66W |
Urea Heating Inlet Water Pipe – Solenoid to Tank |
1 |
| 6 |
1160130-66W |
Electrically Heated Urea Supply Pipe – Pump to Nozzle |
1 |
| 7 |
1160127-28V |
Urea Heating Return Water Pipe |
1 |
| 8 |
1160128-55R |
Urea Heating Inlet Water Pipe – Engine to Solenoid |
1 |
| 9 |
1160315-61S |
Urea Nozzle Cooling Inlet Water Pipe Assembly |
1 |
| 10 |
1160310-61S |
Urea Nozzle Cooling Return Water Pipe Assembly |
1 |
| 11 |
CQ2180625 |
Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw |
3 |
| 12 |
1161210-76W |
Urea Nozzle Assembly |
1 |
| 13 |
1160126-73W |
Urea Nozzle Piping Bracket |
1 |
| 14 |
CQ1460816 |
Combination Bolt |
2 |
| 15 |
1160126-61S |
Urea Pump Piping Bracket |
1 |
| 16 |
CQ1461025 |
Combination Bolt |
1 |
| 17 |
1160126A76R |
Urea Piping Bracket |
1 |
| 18 |
CQ34008 |
Hex Nut |
8 |
| 19 |
1160140-66W |
Urea Tank Strap Assembly |
2 |
| 20 |
1160134-87V |
Strap Liner |
2 |
| 21 |
1160010-76W |
Urea Tank Assembly |
1 |
| 22 |
1160117-66W |
Urea Tank Bottom Liner |
2 |
| 23 |
CQ1500860 |
Hexagon Head Bolt |
3 |
| 24 |
Q40308 |
Spring Washer |
3 |
| 25 |
Q40108 |
Washer |
3 |
| 26 |
1161010-76W |
Urea Pump Assembly |
1 |
| 27 |
Q1841445T |
Hex Flange Bolt (Standard) |
2 |
| 28 |
Q1841455T |
Hex Head Convex Bolt |
2 |
| 29 |
1160126-93B |
Urea Nozzle Piping Bracket |
1 |
| 30 |
1160105-66W |
Urea Tank Bracket Welding Assembly |
1 |
Diagnostic Protocols for Structural Integrity
Inspecting the FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly is a vital part of preventative maintenance. The first step is to check for leaks at the Small Worm Drive Hose Clamp locations. Cold flow of the rubber hoses can cause them to shrink, loosening the clamp tension. A white, crystalline buildup of dried urea indicates a leak that must be addressed immediately by tightening the clamp or replacing the hose.
Structural inspection should focus on the Urea Tank Bracket Welding Assembly and the Urea Pump Piping Bracket. Look for stress cracks near the weld zones or bolt holes. Vibration fatigue is a common enemy in heavy-duty trucks. If a bracket is cracked, it allows the component it supports to vibrate excessively, which will eventually fatigue the rigid fluid lines connected to it.
Finally, examine the condition of the Urea Tank Strap Assembly. Ensure that the Strap Liner is in place and not worn through. Metal-on-plastic contact will quickly abrade the urea tank wall, leading to a puncture. Check the Plastic Cable Ties to ensure they haven’t snapped in the cold, leaving wiring harnesses to dangle and chafe against the chassis.
Conclusion: The Backbone of Emissions Control
The FAW Russian Brackets And Piping assembly is the unsung hero of the truck’s environmental compliance system. By providing rigid support and heated transport for the urea solution, it ensures that the SCR system functions correctly in all weather conditions. The engineering behind the heated lines and vibration-isolating brackets reflects a deep understanding of the challenges posed by the Russian operating environment.
For fleet owners, maintaining this assembly with genuine FAW parts is critical. Generic hoses may lack the integrated heating elements or chemical resistance required for long-term durability. By investing in the authentic FAW Russian Brackets And Piping components, you protect your vehicle from emissions-related downtime and ensure it remains a reliable asset in your logistics fleet.
Packaging and Logistics
FAW parts, including the Cylinder Block Assembly, are packaged with care to ensure safe delivery. Each component is secured in protective materials to prevent damage during transit. The logistics network guarantees timely shipments worldwide, supporting efficient maintenance operations. Below is an image illustrating the standard packaging for FAW truck parts, showcasing the attention to detail in handling and storage.
This packaging approach minimizes the risk of corrosion or impact damage, ensuring that parts like the FAW Cylinder Block Assembly arrive in perfect condition. Customers can rely on FAW’s logistics for consistent quality and reliability.


