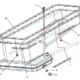
FAW Russian Valve Train Logical: 27 Precision Parts for Unmatched Combustion Efficiency
The FAW Russian Valve Train Logical assembly is the synchronized respiratory system of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z engine. It orchestrates the precise intake of oxygen and evacuation of exhaust gases, ensuring optimal power generation in sub-zero climates. This guide deconstructs the rocker shafts, valves, and solenoids that constitute this complex mechanism, essential for maintaining peak performance in the Russian Federation.

FAW Russian Valve Train Logical
Actuation Architecture: Rocker Shafts and Arms
The backbone of the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical system is the split rocker shaft arrangement. The engine utilizes two distinct assemblies: the Rocker Shaft Assembly (Cyl 1, 2, 3) (Part No. 1007165-51B) and the Rocker Shaft Assembly (Cyl 4, 5, 6) (Part No. 1007175-51B). This split design reduces the torsional stress that would otherwise affect a single long shaft, maintaining consistent valve lift across all cylinders even during high-RPM operations in cold weather.
Mounted on these shafts are the primary actuators: the Intake Valve Rocker Assembly (Part No. 1007110-51B) and the Exhaust Valve Rocker Assembly (Part No. 1007120-51B). These components in the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical feature hardened roller tips to minimize friction against the valve bridge. In the Russian Arctic, where oil viscosity can be high at startup, reducing mechanical friction is crucial to prevent valvetrain wear and ensure immediate engine response.
To secure these shafts against the immense upward force of the cam profile, the system employs robust clamping blocks. The Rocker Shaft Clamp Block (I) (Part No. 1007181-81D), Rocker Shaft Clamp Block (II) (Part No. 1007182-51B), and Rocker Shaft Clamp Block (III) (Part No. 1007183-51B) provide rigid anchor points. These blocks prevent shaft deflection within the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical, ensuring that the precise geometry of the valve lift is maintained without hysteresis or lag.
Precision alignment is further guaranteed by the Rocker Shaft Axial Positioning Sleeve (Part No. 1007163-51B). This sleeve eliminates lateral movement of the rockers along the shaft. By keeping the rockers perfectly centered over the valves, the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical prevents side-loading on the valve stems, a common cause of valve guide wear and oil consumption in heavy-duty engines operating in harsh environments.
Sealing and Return: Valves, Springs, and Bridges
The actual gas exchange is handled by the Intake Valve (Part No. 1007011-81D) and the Exhaust Valve (Part No. 1007016-81D). In the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical, the exhaust valves are friction-welded from bimetallic alloys to withstand temperatures exceeding 700°C. They seat against the Exhaust Valve Seat (Part No. 1003013-81D), a sintered steel ring pressed into the head, designed to resist micro-welding and recession under high-load conditions typical of Russian mining transport.
Because this is a four-valve cylinder head, the system uses a bridging mechanism to actuate two valves simultaneously. The Intake Valve Bridge (Part No. 1007012-81D) and the Exhaust Valve Bridge Assembly (Part No. 1007015-81D) transfer the single rocker arm’s motion to valve pairs. The FAW Russian Valve Train Logical requires these bridges to be perfectly balanced; any unevenness would cause one valve to open slightly before the other, twisting the bridge and potentially bending the valve stems.
Closing the valves is the responsibility of the high-tension springs. The assembly utilizes the Intake Valve Spring (Part No. 1007021-81D) and the specialized Exhaust Valve Inner Spring (Part No. 1007023-81D). The use of nested springs in the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical provides redundancy and prevents valve float at high RPMs. These springs sit on the Valve Spring Seat (Part No. 1007024-81D) and are retained by the Valve Collet (Part No. 1007028-53D), ensuring secure retention even during rapid deceleration.
Oil control is managed by the Valve Stem Seal Assembly (Part No. 1007035-55R), fitted over the Valve Guide (Part No. 1003014-81D). In the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical, these seals are made from fluoro-elastomers that remain flexible at -40°C. A failure here would allow oil to be sucked into the combustion chamber (intake) or blown into the exhaust (exhaust), leading to blue smoke and carbon fouling of the expensive turbocharger turbine wheel.
Engine Braking Logic: The Solenoid Interface
Advanced control within the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical is facilitated by the Solenoid Valve Assembly (Part No. 1007160-51B). This component typically manages the hydraulic circuit for the engine compression brake (Jake brake). In mountainous Russian terrain, this system is vital for safety, allowing the engine to absorb vehicle kinetic energy. The solenoid mounts to the Solenoid Valve Seat (Part No. 1007164-51B), which interfaces directly with the rocker oil galleries.
The sealing of this high-pressure hydraulic circuit is critical. The assembly uses a specific Copper Washer (Part No. Q/WC3403-94) to seal the solenoid connections. In the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical, copper is chosen for its malleability, ensuring a leak-free seal against the pulsating oil pressure used to activate the brake rocker mechanism. A leak here would result in weak or non-existent engine braking performance.
Securement of these electronic components utilizes the Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw (Part No. CQ2180612). The precision of these screws ensures that the solenoid is held firmly against its seat without distorting the valve body. The FAW Russian Valve Train Logical integrates these electronic and hydraulic systems seamlessly into the mechanical valvetrain, providing drivers with reliable retardation power essential for navigating icy descents.
Unused oil passages are sealed off with the Hexagon Head Plug (Part No. CQ61708). While simple, these plugs maintain the integrity of the internal oil pressure. In the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical, maintaining full oil pressure is not just about lubrication; it is about the hydraulic functionality of the engine brake system. Any pressure loss compromises both durability and safety.
Component Breakdown List
The following table provides the comprehensive Bill of Materials for the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical assembly. Precision in selecting replacement parts is mandatory; mismatched rockers or bridges can lead to rapid catastrophic engine failure.
| No. |
Part Number |
Part Name |
Qty |
| 1 |
1007183-51B |
Rocker Shaft Clamp Block (III) |
1 |
| 2 |
Q1841075T |
Hexagon Flange Bolt (Coarse Shank/Standard) |
10 |
| 3 |
1007120-51B |
Exhaust Valve Rocker Assembly |
6 |
| 4 |
1007163-51B |
Rocker Shaft Axial Positioning Sleeve |
6 |
| 5 |
1007110-51B |
Intake Valve Rocker Assembly |
6 |
| 6 |
Q1841080T |
Hexagon Flange Bolt |
4 |
| 7 |
1007164-51B |
Solenoid Valve Seat |
2 |
| 8 |
CQ2180612 |
Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw |
2 |
| 9 |
1007160-51B |
Solenoid Valve Assembly |
2 |
| 10 |
Q/WC3403-94 |
Copper Washer (8X14) |
2 |
| 11 |
CQ61708 |
Hexagon Head Plug |
2 |
| 12 |
1007175-51B |
Rocker Shaft Assembly (Cyl 4, 5, 6) |
1 |
| 13 |
1007182-51B |
Rocker Shaft Clamp Block (II) |
3 |
| 14 |
1007165-51B |
Rocker Shaft Assembly (Cyl 1, 2, 3) |
1 |
| 15 |
1007181-81D |
Rocker Shaft Clamp Block (I) |
1 |
| 16 |
1007012-81D |
Intake Valve Bridge |
6 |
| 17 |
1007028-53D |
Valve Collet |
48 |
| 18 |
1007024-81D |
Valve Spring Seat |
24 |
| 19 |
1003014-81D |
Valve Guide |
24 |
| 20 |
1007021-81D |
Intake Valve Spring |
24 |
| 21 |
1007035-55R |
Valve Stem Seal Assembly |
24 |
| 22 |
1003012-81D |
Intake Valve Seat |
12 |
| 23 |
1007011-81D |
Intake Valve |
12 |
| 24 |
1007016-81D |
Exhaust Valve |
12 |
| 25 |
1003013-81D |
Exhaust Valve Seat |
12 |
| 26 |
1007023-81D |
Exhaust Valve Inner Spring |
12 |
| 27 |
1007015-81D |
Exhaust Valve Bridge Assembly |
6 |
Diagnostic Protocols for Valvetrain Health
Maintaining the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical requires strict adherence to valve lash adjustment intervals. As the Intake Valve and Exhaust Valve pound against their seats, they can recede into the head, tightening the lash. This prevents the valves from closing fully, leading to burnt valves and compression loss. Regular feeler gauge checks on the bridge and rocker arm interfaces are the primary preventative measure against this failure mode.
Inspect the Valve Bridge for uneven wear patterns. If the bridge is tilting or the contact patch with the rocker arm is off-center, it indicates a bent pushrod or a worn Rocker Shaft Assembly bushing. This misalignment causes side-loading on the valve stems, rapidly wearing out the Valve Guide and Valve Stem Seal Assembly, resulting in high oil consumption and blue smoke.
Finally, verify the operation of the Solenoid Valve Assembly if equipped with an engine brake. A clicking sound without braking effect suggests a clogged oil passage or a failed electrical connection at the solenoid. Keeping the oil clean is paramount for the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical, as sludge can block the fine oil ports in the rocker shafts and solenoids, leading to seizure and expensive top-end repairs.
Conclusion: The Rhythm of Reliability
The FAW Russian Valve Train Logical is a masterpiece of synchronized engineering, designed to deliver maximum air and fuel efficiency under the most demanding conditions. Every component, from the hardened tips of the Intake Valve Rocker Assembly to the tension of the Valve Collet, plays a vital role in the engine’s performance. There are no redundant parts in this assembly; each one is a link in the chain of combustion.
For fleet owners operating in the Russian Federation, using genuine FAW replacement parts is the only way to ensure the durability of the FAW Russian Valve Train Logical. Aftermarket valves may lack the bimetallic construction required for heat resistance, and generic springs may fatigue prematurely. By investing in OEM quality, you ensure that your CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck continues to breathe freely and deliver power reliably, mile after frozen mile.
Packaging and Logistics
FAW parts, including the Cylinder Block Assembly, are packaged with care to ensure safe delivery. Each component is secured in protective materials to prevent damage during transit. The logistics network guarantees timely shipments worldwide, supporting efficient maintenance operations. Below is an image illustrating the standard packaging for FAW truck parts, showcasing the attention to detail in handling and storage.
This packaging approach minimizes the risk of corrosion or impact damage, ensuring that parts like the FAW Cylinder Block Assembly arrive in perfect condition. Customers can rely on FAW’s logistics for consistent quality and reliability.