FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic: 16 Precision Components for Unbeatable Synchronization
The FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic is the symphonic conductor of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z engine, ensuring absolute synchronization between piston movement, valve actuation, and fuel injection. In the unforgiving climate of the Russian Federation, this all-gear drive system provides superior reliability compared to belts or chains, resisting stretching and breakage at -40°C. This guide breaks down the complex gear train into its constituent shafts, idlers, and fasteners for precise maintenance.
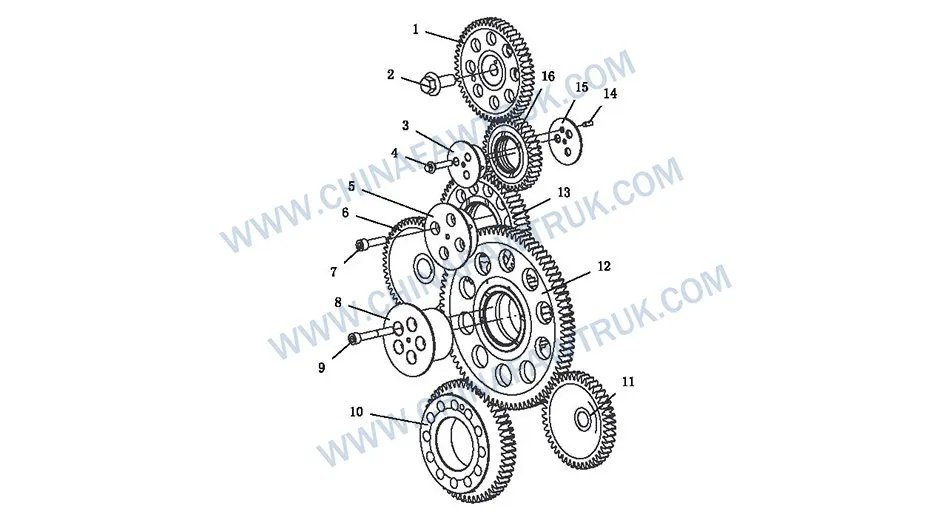
FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic
Master and Slave: Crankshaft and Camshaft Synchronization
At the foundation of the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic lies the Crankshaft Timing Gear (Part No. 1005037-81D). This primary drive gear is shrink-fitted onto the crankshaft nose, converting linear piston motion into rotational timing data. Its helical tooth profile is precision-ground to minimize gear whine and maximize contact area, ensuring that the immense torque required to drive the entire valvetrain is transferred without slippage or tooth deformation under heavy load.
The recipient of this rotational force is the Camshaft Timing Gear (Part No. 1006021-81D). Located at the top of the gear train, it spins at exactly half the speed of the crankshaft to manage the four-stroke combustion cycle. The engagement between these gears within the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic must remain backlash-free to prevent “timing scatter,” which can cause erratic idling and reduced power in cold conditions where fuel atomization is already compromised.
Securing this critical upper gear is the specialized Fastening Bolt – Camshaft Timing Gear (Part No. 1006017-53D). This is not a standard fastener; it is a high-tensile bolt designed to resist the cyclical shear loads generated by the valve springs compressing and releasing. If this bolt were to loosen, the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic would fail instantly, likely resulting in catastrophic valve-to-piston contact that would destroy the engine.
The material science behind the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic involves case-hardened steel alloys. These materials are chosen specifically for their ability to resist surface pitting and spalling. In the Russian Arctic, lubrication can be delayed during startup; these hardened surfaces ensure the gears can survive momentary boundary lubrication conditions without sustaining permanent damage.
The Idler Network: Stack Gears and Shafts
Bridging the gap between the crank and cam is a complex network of idler gears, starting with the Timing Intermediate Stack Gear Assembly (Part No. 1006040-81D). This “stack” gear is a compound unit, often featuring two gear faces to effect a gear reduction or to drive multiple accessories simultaneously. The FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic relies on this component to distribute rotational force to the injection pump and air compressor without overloading a single gear mesh.
Supporting these rotating masses are specialized shafts, such as the Timing Intermediate Gear Shaft (I) (Part No. 1006051-81D) and the Timing Intermediate Gear Shaft (III) (Part No. 1006057-81D). These shafts act as stationary axles upon which the gears rotate, typically riding on pressure-fed bushings. The rigidity of these shafts is paramount; any deflection would misalign the gear teeth, leading to rapid wear and noise within the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic system.
Further along the train, we find the Timing Intermediate Gear (II) (Part No. 1006053-81D) and the Timing Intermediate Gear Assembly (Part No. 1006060-81D). These gears transmit motion laterally across the engine front. The precision of the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic ensures that the backlash (the clearance between mating teeth) is kept within microscopic tolerances, preventing the “clattering” noise often associated with older diesel engines.
Axial movement of these gears is controlled by components like the Timing Intermediate Gear (III) Thrust Plate (Part No. 1006056-81D). This hardened steel plate prevents the gear from “walking” off its shaft under the influence of helical gear thrust forces. In the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic, maintaining axial position is as critical as radial alignment to prevent the gears from machining into the timing cover.
Fuel and Air: Driving Critical Accessories
The FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic is responsible for more than just valve events; it powers the engine’s life support systems. The Fuel Injection Pump Drive Gear (Part No. 1111216-81D) is perhaps the most critical auxiliary component. It drives the high-pressure fuel pump, timing the injection of diesel fuel to the microsecond. A failure or slip here would result in immediate engine shutdown or severe knock.
Simultaneously, the Air Compressor Driven Gear (Part No. 1006047-81D) powers the pneumatic system for the truck’s brakes and suspension. In the context of the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic, this gear must withstand the high pulsating loads of the reciprocating air compressor. The robust tooth profile ensures that braking air pressure is built rapidly, even when the engine is idling in cold weather.
The integration of these accessories directly into the gear train, rather than using belts, is a hallmark of the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic design. Belts can become brittle and snap in -50°C temperatures, whereas steel gears provide fail-safe operation. This direct-drive architecture is a key selling point for reliability in the Russian logistics sector.
Alignment of these accessory gears is finalized by the Cylindrical Pin (Part No. Q5210616). This dowel pin ensures that the accessory housings are perfectly centered relative to the gear train. Any misalignment in the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic auxiliary drive would place excessive side loads on the pump bearings, leading to premature seal failure and leaks.
The Anchors: High-Strength Fastening Strategy
The integrity of the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic is held together by a specific selection of fasteners. The assembly uses the Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw (Part No. CQ2181040TF2 and CQ2181070TF2) for precision clamping. These socket head screws allow for high torque application in tight spaces where a standard hex wrench cannot fit, ensuring the gear shafts are locked solidly to the block.
For larger structural components, the Hexagon Flange Bolt (Part No. Q1840840) is utilized. The flange design distributes the clamping load over a wider area, preventing the bolt head from digging into the gear hubs or thrust plates. In the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic, maintaining consistent clamping force is vital to prevent fretting corrosion between mating surfaces.
These fasteners are treated with anti-corrosion coatings to survive the harsh environment inside the engine, where acidic oil byproducts can attack standard steel. Furthermore, the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic assembly often requires the use of thread-locking compounds on these bolts to prevent them from backing out under the intense high-frequency vibration of the gear train.
Component Breakdown List
The following table lists the complete breakdown of the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic assembly. Precision in part selection is required during overhauls to maintain the intricate timing relationships of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z engine.
| No. |
Part Number |
Part Name |
Qty |
| 1 |
1006021-81D |
Camshaft Timing Gear |
1 |
| 2 |
1006017-53D |
Fastening Bolt – Camshaft Timing Gear |
1 |
| 3 |
1006057-81D |
Timing Intermediate Gear Shaft (III) |
1 |
| 4 |
Q1840840 |
Hexagon Flange Bolt (Coarse/Standard) |
3 |
| 5 |
1006053-81D |
Timing Intermediate Gear (II) |
1 |
| 6 |
1111216-81D |
Fuel Injection Pump Drive Gear |
1 |
| 7 |
CQ2181040TF2 |
Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw |
4 |
| 8 |
1006051-81D |
Timing Intermediate Gear Shaft (I) |
1 |
| 9 |
CQ2181070TF2 |
Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw |
5 |
| 10 |
1005037-81D |
Crankshaft Timing Gear |
1 |
| 11 |
1006047-81D |
Air Compressor Driven Gear |
1 |
| 12 |
1006040-81D |
Timing Intermediate Stack Gear Assembly |
1 |
| 13 |
1006060-81D |
Timing Intermediate Gear Assembly |
1 |
| 14 |
Q5210616 |
Cylindrical Pin |
1 |
| 15 |
1006056-81D |
Timing Intermediate Gear (III) Thrust Plate |
1 |
| 16 |
1006070-81D |
Timing Intermediate Gear Assembly |
1 |
Critical Diagnostics for Gear Train Health
Maintaining the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic begins with auditory diagnostics. A whining sound that increases with RPM often indicates worn teeth or excessive backlash in the Timing Intermediate Gear mesh. This wear exposes the engine to timing drift, which manifests as rough idling and increased fuel consumption. Mechanics should use a stethoscope on the front timing cover to isolate the noise source before teardown.
Visual inspection is possible during major service intervals. Check the Timing Intermediate Gear Shaft surfaces for scoring or blueing, which indicates overheating due to oil starvation. In the cold Russian climate, ensuring that the oil galleries feeding these shafts are free of sludge is paramount. A seized idler shaft within the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic will shear its mounting bolts, leading to catastrophic engine failure.
Finally, verify the torque on all Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screw fasteners. These screws can loosen over time due to the harmonic vibrations of the diesel engine. If a screw backs out, it can fall into the gear mesh, shattering teeth and jamming the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic mechanism. Use of thread locker and adherence to factory torque specs is the only way to guarantee the security of this vital system.
Conclusion: The Heartbeat of the Engine
The FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic is an engineering marvel designed to provide absolute precision in one of the world’s toughest environments. By using a robust all-gear drive instead of belts, FAW ensures that the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z engine remains perfectly synchronized for hundreds of thousands of kilometers. Every component, from the massive Crankshaft Timing Gear to the smallest thrust plate, plays a vital role in this reliability.
For fleet owners, maintaining this system with genuine parts is non-negotiable. Aftermarket gears often lack the precise tooth profile and surface hardening required to survive in the FAW Russian Timing Gear Logic assembly. By investing in OEM quality, you ensure that your trucks continue to deliver the power and efficiency demanded by the Russian logistics industry, regardless of the freezing temperatures they face.
Packaging and Logistics
FAW parts, including the Cylinder Block Assembly, are packaged with care to ensure safe delivery. Each component is secured in protective materials to prevent damage during transit. The logistics network guarantees timely shipments worldwide, supporting efficient maintenance operations. Below is an image illustrating the standard packaging for FAW truck parts, showcasing the attention to detail in handling and storage.
This packaging approach minimizes the risk of corrosion or impact damage, ensuring that parts like the FAW Cylinder Block Assembly arrive in perfect condition. Customers can rely on FAW’s logistics for consistent quality and reliability.


