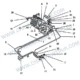
Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW: 32 Componentes de precisão para controle de emissões do Ártico em conformidade
O Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW module is the environmental cornerstone of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z heavy-duty dump truck. Operating in the freezing expanses of the Russian Federation requires more than just a reservoir; it demands a sophisticated thermal management system to prevent Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) from crystallizing at -11°C. This comprehensive guide dissects the electrically heated piping, the precision dosing pump, and the rugged mounting architecture that ensures this SCR (Redução Catalítica Seletiva) system functions flawlessly in sub-zero conditions.

Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW
O reservatório: Storage and Active Heating
O núcleo do sistema é o Montagem do tanque de uréia (Parte não. 1160010-76C). This component is far more complex than a standard fuel tank. No Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW projeto, the reservoir must act as a heating vessel. Urea solution (AdBlue) freezes at -11°C, a temperature frequently exceeded in Russian winters. Para combater isso, the tank is equipped with internal heating elements or coolant loops managed by the Urea Level and Temperature Sensor Assembly (Parte não. 3602525-76W-C00). This sensor provides critical feedback to the ECU, triggering the thawing cycle before the engine is allowed to produce high torque.
The fluid transport out of the tank is managed by a series of specialized lines, como o Tubo de fornecimento de uréia aquecido eletricamente – Tanque para bomba (Parte não. 1160120-66C). Unlike standard fuel lines, these pipes feature integrated resistive heating wires wrapped around the core. This active heating prevents the urea from freezing in the narrow lines during operation, a common failure point in non-arctic spec trucks. O Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW system ensures that the fluid remains liquid from the reservoir all the way to the dosing unit.
Além disso, o sistema inclui o Tubulação de água de entrada de aquecimento de uréia – Motor para Solenóide (Parte não. 1160128-55R) e o Tubo de água de retorno de aquecimento de uréia (Parte não. 1160127-28V). These components utilize the engine’s waste heat to maintain the tank temperature during long hauls. This dual-heating strategy—electrical for startup and coolant for running—is a hallmark of the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW engineering, maximizing energy efficiency while guaranteeing emissions compliance.
The structural material of the tank is a high-density polyethylene (PEAD) or similar robust polymer, chosen for its chemical resistance to the corrosive nature of urea. No entanto, plastics can become brittle in extreme cold. The specific formulation used in the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW is impact-modified to withstand the shocks and vibrations of off-road dump truck operations at -40°C without cracking.
Precision Injection: Pump and Nozzle Dynamics
Pressurizing the fluid is the responsibility of the Conjunto de bomba de uréia (Parte não. 1161010-76C). This precision diaphragm pump must deliver exact quantities of urea to the exhaust stream based on real-time NOx sensor data. No Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW sistema, the pump is also capable of reversing flow. When the engine is turned off, the pump purges the lines, sucking the urea back into the tank to prevent it from freezing and expanding in the delicate nozzle or lines.
The atomization of the fluid occurs at the Conjunto de bico de ureia (Parte não. 1161210-76C). This injector sits directly in the hot exhaust stream. To prevent the nozzle itself from overheating or clogging with crystallized urea, it is cooled by the Conjunto de tubulação de água de entrada de resfriamento do bocal de ureia (Parte não. 1160315-61S) e o Conjunto de tubo de água de retorno de resfriamento do bocal de ureia (Parte não. 1160310-61S). This active liquid cooling is vital for the longevity of the nozzle in the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW ecossistema.
Connecting the pump to the nozzle is the Tubo de fornecimento de uréia aquecido eletricamente – Bomba para bocal (Parte não. 1160130-66C). Like the suction side, this pressure line is electrically heated. The connectors on these lines are specialized quick-connect fittings that must be handled with care. A damaged connector in the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW circuit usually requires replacing the entire heated line assembly, which is a costly repair.
Securement of these components is critical. O Suporte de tubulação para bico de ureia (Parte não. 1160126-73C) e o Suporte de tubulação da bomba de uréia (Parte não. 1160126-61S) ensure that the lines do not vibrate against the chassis. Vibration can wear through the heating element insulation, causing short circuits. The rigid mounting provided by these brackets ensures the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW system remains intact over thousands of kilometers of rough terrain.
Lógica de montagem: Correias, Liners, e colchetes
The physical security of the tank is maintained by the Conjunto de alça do tanque de ureia (Parte não. 1160140-66C). These stainless steel straps wrap around the tank, holding it against the chassis brackets. No Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW instalação, metal-to-plastic contact is avoided by using the Forro de cinta (Parte não. 1160134-87V). This rubber interface prevents the straps from cutting into the polymer tank and provides vibration damping.
Supporting the tank from below is the Forro inferior do tanque de uréia (Parte não. 1160117-66C) e o Conjunto de soldagem de suporte de tanque de ureia (Parte não. 1160105-66C). This heavy-duty framework is bolted to the truck frame. Given the harsh corrosive environment of Russian roads, where salts are used liberally, these brackets are typically coated with advanced anti-corrosion treatments to prevent structural failure.
The fasteners used, como o Parafuso de flange hexagonal (Parte não. Q1841445T) e o Parafuso de combinação (Parte não. CQ1461025), are high-tensile units. The flange head design distributes the clamping load, ensuring the brackets do not shift. Checking the torque on these bolts is a standard maintenance procedure for the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW, as a loose tank can damage the delicate electrical and fluid connections.
Cable management is handled by the Abraçadeira de plástico (Parte não. T67417246). Há 24 of these specified, highlighting the complexity of the wiring and plumbing harness. No Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW sistema, proper routing and securing of the heated lines are essential to prevent chafing and electrical shorts, which could disable the heating system and freeze the unit.
Lista detalhada de componentes
A tabela a seguir fornece o completo, exhaustive breakdown of the Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW módulo. Inclui todos 32 components identified in the assembly diagrams, ensuring that every bracket, sensor, and bolt is accounted for during maintenance or repair.
| Não. |
Número da peça |
Nome da peça |
Quantidade |
| 1 |
T67417246 |
Abraçadeira de plástico |
24 |
| 2 |
1160120-66C |
Tubo de fornecimento de uréia aquecido eletricamente – Tanque para bomba |
1 |
| 3 |
1160250-66C |
Tubo de fornecimento de uréia aquecido eletricamente – Bomba para tanque |
1 |
| 4 |
CQ67625 |
Braçadeira de mangueira de acionamento sem-fim pequeno |
6 |
| 5 |
1160129-66C |
Tubulação de água de entrada de aquecimento de uréia – Solenóide para Tanque |
1 |
| 6 |
1160130-66C |
Tubo de fornecimento de uréia aquecido eletricamente – Bomba para bocal |
1 |
| 7 |
1160127-28V |
Tubo de água de retorno de aquecimento de uréia |
1 |
| 8 |
1160128-55R |
Tubulação de água de entrada de aquecimento de uréia – Motor para Solenóide |
1 |
| 9 |
1160315-61S |
Conjunto de tubulação de água de entrada de resfriamento do bocal de ureia |
1 |
| 10 |
1160310-61S |
Conjunto de tubo de água de retorno de resfriamento do bocal de ureia |
1 |
| 11 |
CQ2180625 |
Parafuso de cabeça sextavada |
3 |
| 12 |
1161210-76C |
Conjunto de bico de ureia |
1 |
| 13 |
1160126-73C |
Suporte de tubulação para bico de ureia |
1 |
| 14 |
CQ1460816 |
Parafuso de combinação |
2 |
| 15 |
1160126-61S |
Suporte de tubulação da bomba de uréia |
1 |
| 16 |
CQ1461025 |
Parafuso de combinação |
1 |
| 17 |
1160126A76R |
Suporte de tubulação de uréia |
1 |
| 18 |
CQ34008 |
Noz hexadecimal |
8 |
| 19 |
1160140-66C |
Conjunto de alça do tanque de ureia |
2 |
| 20 |
1160134-87V |
Forro de cinta |
2 |
| 21 |
1160010-76C |
Montagem do tanque de uréia |
1 |
| 21-1 |
1160015-76W-C00 |
Urea Tank Sub-assembly |
1 |
| 21-2 |
3602525-76W-C00 |
Urea Level and Temperature Sensor Assembly |
1 |
| 22 |
1160117-66C |
Forro inferior do tanque de uréia |
2 |
| 23 |
CQ1500860 |
Parafuso de cabeça hexagonal |
3 |
| 24 |
Q40308 |
Arruela elástica |
3 |
| 25 |
Q40108 |
Máquina de lavar |
3 |
| 26 |
1161010-76C |
Conjunto de bomba de uréia |
1 |
| 27 |
Q1841445T |
Parafuso de flange hexadecimal (Padrão) |
2 |
| 28 |
Q1841455T |
Parafuso convexo de cabeça sextavada |
2 |
| 29 |
1160126-93B |
Suporte de tubulação para bico de ureia |
1 |
| 30 |
1160105-66C |
Conjunto de soldagem de suporte de tanque de ureia |
1 |
Diagnostic Protocols for SCR Health
Inspecionando o Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW requires checking for white crystalline deposits. These crystals, formed by dried urea, are the enemy of the system. If found around the Conjunto de bomba de uréia or hose connections, they indicate a leak. No tempo frio, even a small leak can freeze and expand, cracking the expensive pump housing. Cleaning these deposits with warm water is the first step in diagnosis.
Test the heating circuits regularly. With the ignition on and the engine cold, check the resistance of the Tubo de fornecimento de uréia aquecido eletricamente conectores. An open circuit means the heater wire is broken, and the pipe must be replaced. A frozen pipe will trigger a “Reductant Pressure Too Low” fault code and derate the engine.
Finalmente, verify the integrity of the Conjunto de alça do tanque de ureia. Road salt accumulation under the straps can cause them to rot. If a strap snaps, the tank can shift, stressing the rigid coolant lines and causing a coolant leak. Certifique-se de que Forro de cinta is intact to prevent metal-on-plastic abrasion that could puncture the tank.
Conclusão: Compliance in the Cold
O Tanque Russo de Ureia FAW is a sophisticated chemical storage and delivery system designed to operate where other systems fail. Its integrated heating logic and robust material selection ensure that emissions compliance is maintained even in the depths of the Russian winter.
Para proprietários de frotas, the cost of neglecting this system is high. A frozen urea tank leads to engine power loss and potential fines. By using genuine FAW replacement parts, including the specific heated lines and cold-weather sensors, you protect your investment and ensure your vehicles remain productive and compliant, no matter the temperature.
Embalagem e Logística
Peças FAW, incluindo o conjunto do bloco de cilindros, são embalados com cuidado para garantir uma entrega segura. Cada componente é protegido por materiais de proteção para evitar danos durante o transporte. A rede logística garante envios pontuais em todo o mundo, apoiando operações de manutenção eficientes. Abaixo está uma imagem ilustrando a embalagem padrão para peças de caminhão FAW, mostrando a atenção aos detalhes no manuseio e armazenamento.
Esta abordagem de embalagem minimiza o risco de corrosão ou danos por impacto, garantindo que peças como o conjunto do bloco de cilindros FAW cheguem em perfeitas condições. Os clientes podem confiar na logística da FAW para obter qualidade e confiabilidade consistentes.