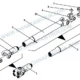
Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW: Ingeniería 7 Vínculos estratégicos para una propulsión imparable en el Ártico
El Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW outlines the complex torque distribution network for the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z 6×6 camión volcado. This technical guide dissects the transfer case connections, front steering drive, and rear tandem axle linkages. We analyze the 7 critical components that ensure kinetic continuity and vibration-free power delivery in the -40°C conditions of the Siberian mining sector.

Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW
Arquitectura del sistema: el 6×6 Disposición
The drivetrain architecture depicted in the Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW is a testament to heavy-duty engineering designed for low-traction environments. Unlike standard 6×4 trucks that simply power the rear bogie, this system involves a complex routing of torque to all six wheel positions. The central hub of this distribution is the Transfer Case Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly (Número de pieza. 2215010-55R). This specific shaft connects the main transmission output to the transfer case input. It is the single most stressed component in the driveline, as it must transmit 100% of the engine’s torque before it is split between the front and rear axles.
El “55R” designation found throughout the Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW indicates a specific cold-weather modification. In standard driveshafts, the rubber boots protecting the slip yokes and the grease seals within the universal joint caps can freeze and crack in extreme sub-zero temperatures. The Russian-spec components utilize low-temperature synthetic elastomers and are pre-packed with lithium-complex grease that retains viscosity down to -50°C. This ensures that the needle bearings within the U-joints remain lubricated during the critical first minutes of operation in a frozen quarry.
Además, el Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW highlights the necessity of precise phasing. The driveshafts must be balanced dynamically to prevent harmonic vibrations. In a long-wheelbase dump truck, a vibrating driveshaft acts like a tuning fork, transmitting destructive energy into the transfer case bearings and the differential pinions. The assembly logic dictates that the yokes on either end of the shaft must be aligned (in phase) to cancel out the non-uniform velocity inherent in universal joint rotation. This attention to kinematic detail is what separates a smooth-running truck from one that shakes itself apart on the highway.
Axle Integration: Front and Intermediate Links
Extending forward from the transfer case is the Front Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly (Número de pieza. 2203010-55R). This component faces unique challenges shown in the Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW. Because the front axle steers, the input angle of the driveshaft changes constantly as the suspension cycles and the truck corners. To accommodate this, the front shaft typically features a high-articulation slip yoke with extended travel. This allows the shaft to lengthen and shorten significantly without bottoming out or pulling apart, maintaining positive engagement even when the front suspension is at full droop during off-road articulation.
Moving rearward, el Middle Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly (Número de pieza. 2205010-55R) connects the transfer case rear output to the first rear drive axle (the middle axle). This shaft is often the longest in the system and is susceptible to “whirl”—a phenomenon where the center of the shaft bows outward at high speeds due to centrifugal force. El Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW dictates a specific tube wall thickness and diameter for this component to raise its critical speed well above the truck’s maximum operating velocity.
The structural integrity of these shafts relies on the quality of the welding between the tube and the yoke. En el Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW contexto, these welds must be free of porosity and stress risers. En el Ártico ruso, thermal contraction can induce tension in the steel. If a weld is weak, the sudden torque application of a differential lock engagement can shear the yoke off the tube. FAW utilizes friction welding or high-precision arc welding to fuse these components, creating a monolithic structure capable of handling torque spikes exceeding 20,000 Nuevo Méjico.
Inter-Axle Dynamics: The Rear Linkage
The shortest yet most active component in the Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW es el Eje de transmisión del eje trasero y conjunto de junta universal (Número de pieza. 2201010-2000). This shaft connects the through-shaft of the middle axle to the input of the rear axle. Because the rear bogie suspension allows the axles to move independently (walking beam action), the working angles of this short shaft are extreme. It must handle sharp angularity changes thousands of times per kilometer as the truck negotiates potholes and ruts.
To survive this grueling duty cycle, the universal joints on this specific shaft are often upgraded to “trabajo pesado” specifications, featuring larger trunnions and more robust needle rollers. El Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW implies a distinct maintenance protocol for this part; because of the steep angles, the U-joints generate more heat. Regular greasing is essential to flush out contaminants and replenish the lubricant film. Neglecting this short shaft is the most common cause of driveline vibration in tandem-axle trucks.
El “2000” suffix in the part number may indicate a specific torque rating or length class tailored to the J6P chassis geometry. El Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW ensures that this shaft is perfectly matched to the inter-axle distance. If an incorrect length shaft is installed, it can bottom out against the differential housing when the truck is fully loaded, transferring suspension impact loads directly into the pinion bearings, leading to catastrophic differential failure.
Connection Security: Pernos de brida y contratuercas
The reliability of the entire propulsion system hinges on the fasteners identified in the Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW. La asamblea utiliza Perno de brida de cabeza hexagonal (Número de pieza. Q1851455T) y Perno de brida de cabeza hexagonal (Número de pieza. Q1851450T). Estos no son tornillos estándar.; they are high-tensile, fine-thread flange bolts designed specifically for driveline flanges. The fine threads allow for higher clamping force, while the flange head distributes this force over a wider area, preventing the bolt from embedding into the yoke metal.
Securing these bolts are the Tipo 1 Non-metallic Insert Hex Lock Nut (Número de pieza. Q32914). el uso de 32 of these nuts confirms that every flange connection is redundant and secure. The non-metallic insert (nylon ring) creates a prevailing torque that prevents the nut from backing off under the severe vibration of the driveshaft. En el Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW lógica, these are single-use items. Once removed for maintenance, the nylon insert loses its elasticity and cannot guarantee a secure lock, necessitating replacement.
The sheer strength of these fasteners is calculated to exceed the friction grip of the flange faces. The torque is transmitted through the friction between the mating flanges, not by the shear strength of the bolts themselves. Por lo tanto, proper torque application is critical. El Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW specifies fasteners that can withstand the high torque settings required to “soldar” the flanges together frictionally, ensuring that the driveshaft becomes a seamless extension of the transmission output.
Desglose de componentes: 123. Driveshaft Assembly
| No. |
Número de pieza |
Nombre de la pieza |
Cantidad |
| 1 | Q32914 | Tipo 1 Non-metallic Insert Hex Lock Nut | 32 |
| 2 | Q1851455T | Perno de brida de cabeza hexagonal | 8 |
| 3 | 2215010-55R | Transfer Case Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly | 1 |
| 4 | 2203010-55R | Front Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly | 1 |
| 5 | 2205010-55R | Middle Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly | 1 |
| 6 | 2201010-2000 | Eje de transmisión del eje trasero y conjunto de junta universal | 1 |
| 7 | Q1851450T | Perno de brida de cabeza hexagonal | 12 |
Conclusión: The Kinetic Backbone
El Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW is more than a parts list; it is the kinetic backbone of the vehicle’s all-terrain capability. Estos 7 components work in unison to translate engine power into forward motion, navigating the complex geometry of a 6×6 chassis with precision and durability. From the cold-resistant rubber boots to the high-tensile flange bolts, every element is engineered to withstand the unique challenges of the Russian operational theater.
Para los gerentes de flota, el Diagrama de conjunto del eje de transmisión ruso FAW serves as a critical guide for preventative maintenance. Regular inspection of the U-joints for play, ensuring flange bolts are torqued to spec, and greasing the slip yokes can prevent costly downtime. By utilizing the genuine parts specified in this assembly, operators ensure that their trucks maintain the robust, reliable propulsion necessary to conquer the toughest jobs on earth.
Embalaje y Logística
piezas FAW, incluido el conjunto del bloque de cilindros, Se empaquetan con cuidado para garantizar una entrega segura.. Cada componente está asegurado con materiales protectores para evitar daños durante el transporte.. La red logística garantiza envíos puntuales en todo el mundo., apoyando operaciones de mantenimiento eficientes. A continuación se muestra una imagen que ilustra el embalaje estándar de las piezas de camiones FAW., mostrando la atención al detalle en el manejo y almacenamiento.
Este enfoque de embalaje minimiza el riesgo de corrosión o daños por impacto., asegurando que piezas como el conjunto de bloque de cilindros FAW lleguen en perfectas condiciones. Los clientes pueden confiar en la logística de FAW para obtener calidad y confiabilidad constantes.