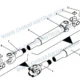
FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft: Decoding 8 Essential Links for Heavy-Duty Articulation
The FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft assembly is the compact powerhouse of the tandem drive system on the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck. Connecting the through-shaft of the middle axle to the input pinion of the rear axle, this component operates under the most extreme geometric stress of any driveline part. In the frozen, undulating terrain of the Russian Federation, where rear bogie articulation puts immense strain on u-joints, the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft ensures uninterrupted torque transfer. This guide deconstructs the 8 strategic components, from the high-angle cross shafts to the precision-welded spline sleeves, that define its rugged capability.

FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft Assembly
System Architecture: The Short-Coupled Challenge
The complete unit is identified as the Rear Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly (Part No. 2201010-2000). The specific suffix “2000” in the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft nomenclature indicates a heavy-duty torque rating, designed to handle the multiplied torque output from the middle axle’s inter-axle differential. This shaft is significantly shorter than the main driveshafts, which introduces unique engineering challenges. In a short shaft, even minor vertical movements of the suspension translate into drastic changes in operating angle.
The FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft is engineered to accommodate the “walking beam” action of the rear suspension. As the truck traverses the rocky, uneven ground of a Siberian mine, the rear axles oscillate independently. The driveshaft must telescope (lengthen and shorten) rapidly while transmitting full power. If the structural rigidity of the shaft tube is insufficient, or if the slip yoke binds, the suspension forces are transmitted directly into the differential bearings, leading to catastrophic failure.
To mitigate this, the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft utilizes components with optimized geometry. The yokes are designed with deeper throats to allow for higher degrees of articulation without binding (yoke-to-yoke interference). This high-angle capability is essential for preventing “driveline bind” when the truck is fully articulated in a cross-axle situation. The robust construction of the 2201010-2000 assembly ensures that the kinetic link between the axles remains unbroken, even when the chassis is twisted to its limits.
Articulation Logic: Cross Shafts and Needle Bearings
The pivot capability of the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft is provided by two units of the Cross Shaft and Needle Roller Bearing Assembly (Part No. 2201030-1050). These universal joint kits, often referred to as spiders, are the focal points of stress. Because of the steep working angles inherent in the rear bogie design, these cross shafts rotate through a wider arc than the main driveshaft joints. This increased angular velocity generates significant heat within the needle bearing cups.
To combat this thermal stress, the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft cross shafts are forged from premium alloy steel, case-hardened to provide a wear-resistant surface for the needle rollers while maintaining a tough core to resist shock loads. The bearing cups are sealed with advanced multi-lip elastomers designed to keep the specific high-temperature grease inside and contaminants out. In the abrasive slurry of a Russian spring thaw, seal integrity is the primary factor determining the lifespan of the U-joint.
Precise positioning of the cross shaft is achieved via Snap Rings (Part Nos. 2201041-80A through 2201048-80A). These rings are manufactured in graduated thicknesses. During the assembly of the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft, technicians select the exact ring thickness required to center the cross shaft within the yoke ears. This “selective assembly” technique eliminates lateral play, ensuring the driveshaft spins on its true geometric center. Even a small offset here would create a severe vibration that could loosen flange bolts.
Extension Logic: Spline Shafts and Tubes
The telescoping function of the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft is managed by the interaction between the Spline Shaft Yoke Assembly (Part No. 2201020-80A) and the Rear Axle Driveshaft Tube, Welded Yoke and Spline Sleeve Assembly (Part No. 2201015-80A). The suffix “80A” suggests a standardized heavy-duty spline profile used across the FAW J6 platform. This slip joint must transmit torque while simultaneously lengthening and shortening as the axles move.
The internal splines of the sleeve are coated with a friction-reducing material, typically a Nylon or Rilsan glide coat. This coating is vital for the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft. Without it, the high torque load would cause the metal splines to bind (spline lock), preventing the shaft from changing length. If the shaft cannot compress when the suspension compresses, it acts as a solid battering ram, driving the differential pinion gear through the housing. The low-friction coating ensures smooth plunging action even under full engine load.
Protection of this critical interface is provided by a specialized dust boot and seal arrangement integrated into the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft. In the extreme cold of -40°C, standard rubber boots can stiffen and crack. The materials used in the Russian-spec assembly are formulated to remain flexible, ensuring a tight seal against ice, water, and road salt. Keeping the splines clean and lubricated is the single most effective way to prevent driveline “clunk” and vibration.
Connection Logic: Flanges and Balance Weights
Connecting the driveshaft to the axles is the Flange Yoke (Part No. 2201023-2000). This heavy steel forging features a serrated face (Hirth coupling style) to mate securely with the axle input flanges. The “2000” series flange is designed with a larger bolt circle diameter to accommodate higher torque loads. The rigidity of this flange is crucial for the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft; any flexing at the connection point would lead to bolt fatigue and eventual joint separation.
Despite its rugged construction, the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft is a precision instrument. Dynamic balance is critical. Because the shaft spins at high RPMs, any mass imbalance creates centrifugal force that vibrates the entire vehicle. To correct this, Balance Sheets (Part Nos. 2201071-1H through 2201079-1H) are spot-welded to the tube. These weights are available in minute increments, allowing the factory to fine-tune the balance of the assembly to within grams.
The short length of the FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft makes balancing particularly challenging but essential. A short, unbalanced shaft creates a high-frequency buzz that can loosen chassis bolts and damage sensitive electronics. The secure welding of the balance weights ensures they remain attached even when the shaft is bombarded by stones and ice on unpaved Russian roads. Checking for missing weights is a key inspection point during servicing.
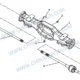
Component Breakdown: 127. Rear Axle Drive Shaft
| No. |
Part Number |
Part Name |
Qty |
| – | 2201010-2000 | Rear Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Assembly | 1 |
| 1 | 2201050-2000 | Spline Shaft Yoke and Universal Joint Assembly | 1 |
| 2 | 2201060-2000 | Rear Axle Driveshaft and Universal Joint Sub-assembly | 1 |
| 3 | 2201023-2000 | Flange Yoke | 1 |
| 4 | 2201030-1050 | Cross Shaft and Needle Roller Bearing Assembly | 2 |
| 5 | 2201041-80A | Snap Ring (Various Thicknesses) | 8 |
| 6 | 2201071-1H | Balance Sheet (Various Weights) | As Req |
| 7 | 2201020-80A | Spline Shaft Yoke Assembly | 1 |
| 8 | 2201015-80A | Rear Axle Driveshaft Tube, Welded Yoke and Spline Sleeve Assembly | 1 |
Conclusion: The Critical Link
The FAW Russian Rear Axle Driveshaft is a deceptively simple component that performs one of the most demanding tasks in the powertrain. It bridges the dynamic gap between the tandem axles, accommodating extreme angles while transmitting massive torque. Its robust construction, characterized by cold-weather seals and precision balancing, ensures that the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z remains operational in the harshest Siberian conditions.
For fleet maintenance, the focus must be on lubrication and inspection. Keeping the U-joints and splines greased with the correct low-temperature lubricant is the most effective way to prevent wear. Neglecting this assembly leads quickly to vibration, seal failure, and costly downtime. By utilizing genuine FAW replacement parts, operators ensure that their trucks maintain the factory-engineered capability to conquer any terrain.
Packaging and Logistics
FAW parts, including the Cylinder Block Assembly, are packaged with care to ensure safe delivery. Each component is secured in protective materials to prevent damage during transit. The logistics network guarantees timely shipments worldwide, supporting efficient maintenance operations. Below is an image illustrating the standard packaging for FAW truck parts, showcasing the attention to detail in handling and storage.
This packaging approach minimizes the risk of corrosion or impact damage, ensuring that parts like the FAW Cylinder Block Assembly arrive in perfect condition. Customers can rely on FAW’s logistics for consistent quality and reliability.