Lógica do sensor do eixo traseiro russo FAW: Salvaguarda 12 Elementos de precisão para integridade de dados ABS impecável
O Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW logic assembly acts as the digital nervous system for the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck’s braking architecture. Operating in the unforgiving Siberian climate requires more than just mechanical strength; it demands precise electronic feedback. This assembly captures critical wheel speed data, enabling the Anti-Lock Braking System (Abs) to modulate pressure and prevent hazardous skids on icy gradients. Ensuring the calibration and protection of the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW is the single most important factor in maintaining vehicle stability control during winter operations.
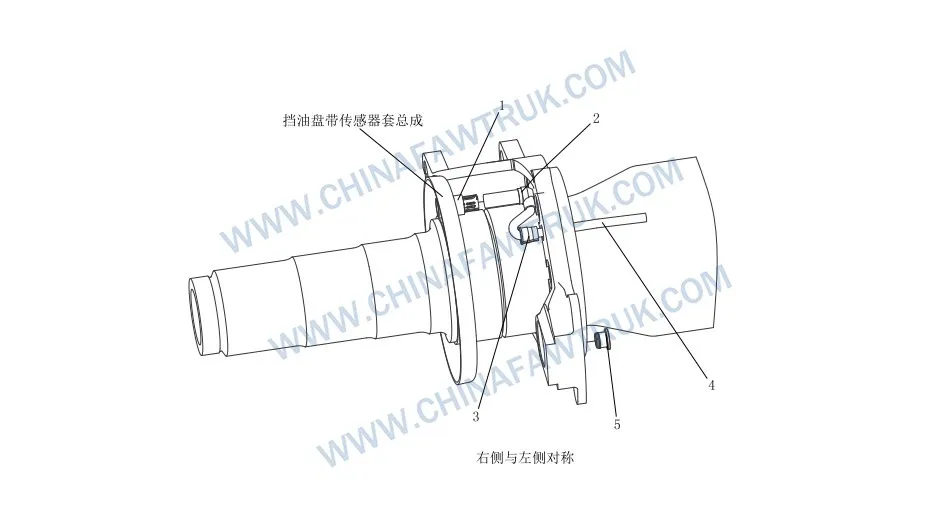
Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW
| Não. |
Número da peça |
Nome da peça |
Quantidade |
| 1 | 3550361-6S | Sensor Sleeve | 2 |
| 2 | 3550360-6S | Conjunto do sensor de velocidade da roda | 2 |
| 3 | 3550381Ba0s | Positioning Sleeve | 4 |
| 4 | 3550351Ba0s | Rubber Protective Sleeve | 2 |
| 5 | 3502861-A0b | Plugue – Rear Brake Bracket | 2 |
A tecnologia central: Inductive Speed Sensing
No epicentro do Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW montagem lógica é o Conjunto do sensor de velocidade da roda (Parte não. 3550360-6S). This component utilizes variable reluctance technology to detect the rotational velocity of the wheel hub. As the exciter ring (tone wheel) rotates with the hub, its teeth pass through the sensor’s magnetic field, inducing an AC voltage signal. The frequency of this signal is directly proportional to wheel speed. No contexto do Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW, the coil windings and internal magnets are encapsulated in a specialized resin. This potting process is critical for the Russian “Zona Fria” especificação, as it prevents thermal shock from fracturing the internal copper windings when the sensor transitions from -50°C ambient air to the radiant heat of the brake drum.
The signal integrity of the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW is paramount for the functioning of the EBS (Electronic Braking System) and ABS. If the sensor signal is erratic or lost, the ECU defaults to a non-ABS mode, which can be catastrophic on icy roads. O Conjunto do sensor de velocidade da roda features a high-grade, shielded cable that resists electromagnetic interference (EMI) from the truck’s alternator and transmission retarder. Além disso, the cable jacketing is formulated from cross-linked polyethylene to maintain flexibility at cryogenic temperatures, preventing the insulation from cracking and shorting out due to chassis articulation.
O Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW assembly is designed for redundancy and reliability. The sensor head is hermetically sealed to IP69K standards, allowing it to withstand high-pressure washdowns and submersion in slush. This level of protection is essential because the rear axle sensors are constantly bombarded by road spray containing corrosive de-icing salts. By maintaining a clean, strong signal, o Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW allows the truck’s computer to make micro-adjustments to brake pressure milliseconds before a wheel lockup occurs, preserving steering authority and preventing jackknifing.
Precisão de montagem: The Critical Air Gap
O desempenho do Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW is entirely dependent on its physical positioning relative to the tone ring. This relationship is managed by the Sensor Sleeve (Parte não. 3550361-6S) e o Positioning Sleeve (Parte não. 3550381Ba0s). These components create a friction-fit interface that holds the sensor securely while allowing for initial calibration. The air gap—the distance between the sensor tip and the tone ring tooth—must be microscopic, typically less than 0.7mm. O Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW uses the positioning sleeve to maintain this gap dynamically.
In the heavy-duty environment of a dump truck, wheel bearings have a designated amount of play, and the axle housing flexes under load. A rigid mount would destroy the sensor immediately upon contact with the rotating ring. O Positioning Sleeve no Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW assembly acts as a specific clutch mechanism. It holds the sensor tight enough to prevent it from backing out due to vibration but allows it to be pushed back if the tone ring touches it due to bearing runout. Esse “push-out” capability is a fail-safe feature of the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW projeto, sacrificing the air gap setting rather than shearing off the sensor head.
The material composition of the Sensor Sleeve utilizes a beryllium-copper alloy or stainless steel spring material that retains its tension properties in extreme cold. Standard spring steel can lose its clamping force or become brittle in the Russian winter. By using these advanced materials, o Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW ensures that the sensor does not vibrate loose on corrugated haul roads. A loose sensor generates a “noisy” signal that the ECU interprets as a fault, leading to false ABS activation or system shutdown.
Environmental Defense: Sealing and Protection
A localização do Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW on the wheel end exposes it to the harshest elements imaginable: lama, pedras, gelo, and intense heat. Para combater isso, a montagem inclui o Rubber Protective Sleeve (Parte não. 3550351Ba0s). This boot fits over the cable exit and the sensor body, preventing water from wicking down the cable and entering the sensor housing. No Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW especificação, this rubber is a silicone-based EPDM compound that stays flexible at -50°C, ensuring the seal is never compromised by cracking.
Além disso, the brake bracket itself acts as a shield, but it requires sealing to prevent the ingress of conductive brake dust. O Plugue – Rear Brake Bracket (Parte não. 3502861-A0b) seals the access ports used for sensor installation. If this plug is missing, magnetic brake dust accumulates on the magnetic tip of the Conjunto do sensor de velocidade da roda. This accumulation, known as “fuzzing,” alters the magnetic field and dampens the signal voltage. O Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW relies on these plugs to keep the sensing environment clean and accurate.
A integridade do Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW wiring harness is also critical. The cable routing paths are designed to avoid pinch points during suspension travel. The assembly instructions dictate specific strain relief loops to prevent the cable from being pulled tight when the axle drops to full extension. Any breach in the cable insulation allows brine to enter the copper strands, levando a “black wire corrosion” that can travel meters up the harness, destruindo o Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW connection at the chassis harness interface.
Diagnostics and Maintenance Strategy
Solução de problemas do Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW requires an understanding of its resistance and voltage characteristics. Technicians typically measure the resistance of the Conjunto do sensor de velocidade da roda (geralmente entre 1000 e 2000 ohms) to check for open circuits or shorts. No entanto, the most definitive test for the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW is measuring the AC voltage output while spinning the wheel. A healthy sensor should generate a clean sine wave that increases in amplitude and frequency with wheel speed.
Ao substituir componentes, o Positioning Sleeve (Parte não. 3550381Ba0s) e Sensor Sleeve (Parte não. 3550361-6S) must always be replaced along with the sensor. Reusing old sleeves is the leading cause of sensor migration and signal dropout. No Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW maintenance protocol, the sensor bore in the bracket must be thoroughly cleaned of rust and old grease before installing the new sleeves. Using a conductive anti-seize paste is strictly prohibited as it interferes with the grounding and signal purity of the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW.
Finalmente, visual inspection of the Rubber Protective Sleeve e Plugue – Rear Brake Bracket should be part of every brake service. Preventing contamination is far cheaper than diagnosing intermittent ABS faults. By adhering to these protocols and using genuine parts for the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW, fleet operators ensure that the vehicle’s safety systems remain vigilant, protecting the driver and the asset on every trip.
Conclusão: The Data Behind the Stopping Power
O Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW logic assembly is a small but indispensable cluster of components. While it lacks the physical mass of the brake drums or shoes, its role in managing the vehicle’s kinetic energy is equally significant. O 12 componentes, incluindo o Conjunto do sensor de velocidade da roda e o crítico Positioning Sleeve, form a cohesive unit that translates mechanical motion into digital safety data.
Para equipes de manutenção de frota, treating the Sensor de eixo traseiro russo FAW with the same respect as the mechanical friction components is essential. A truck with powerful brakes but no ABS control is a liability on ice. By investing in genuine replacement sensors and ensuring precise installation, operators guarantee that their FAW J6P trucks maintain the intelligent control necessary to navigate the hazardous conditions of the Russian heavy transport sector.
Embalagem e Logística
Peças FAW, incluindo o conjunto do bloco de cilindros, são embalados com cuidado para garantir uma entrega segura. Cada componente é protegido por materiais de proteção para evitar danos durante o transporte. A rede logística garante envios pontuais em todo o mundo, apoiando operações de manutenção eficientes. Abaixo está uma imagem ilustrando a embalagem padrão para peças de caminhão FAW, mostrando a atenção aos detalhes no manuseio e armazenamento.
Esta abordagem de embalagem minimiza o risco de corrosão ou danos por impacto, garantindo que peças como o conjunto do bloco de cilindros FAW cheguem em perfeitas condições. Os clientes podem confiar na logística da FAW para obter qualidade e confiabilidade consistentes.