Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW: Liberando 35 Componentes Estratégicos para o Domínio do Torque Ártico
O Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW architecture defines the heavy-duty propulsion capabilities of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z model. Engineered specifically for the Siberian mining sector, this system manages extreme torque loads while navigating sub-zero temperatures. It integrates precise metallurgy with pneumatic locking logic to ensure kinetic continuity on frozen terrain. This technical guide breaks down the assembly to its atomic level, highlighting the maintenance protocols necessary for Arctic endurance.

Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW
Geometric Precision of the Active Bevel Gear
The primary driver of the middle axle’s torque multiplication is the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW (Parte não. 2502036BA6E). This component is machined from high-grade carburized alloy steel, designed to withstand the immense shear forces present in 6×6 JUMPT TRIACTERIOS. The gear teeth feature a specialized spiral profile that maximizes surface contact area. This design choice is critical for reducing point-loading stress, which can lead to premature metal fatigue during high-torque, low-speed maneuvers in open-pit mines.
O Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW operates in a synchronized mesh with the Driven Cylindrical Gear (Parte não. 2502108-A6E). The relationship between these two gears dictates the efficiency of the entire driveline. In the Russian “55R” especificação, the backlash tolerance is tighter than standard models to account for the viscosity changes in gear oil at -50°C. Precise meshing ensures that power is transferred smoothly without the “conversa” that can shatter brittle frozen metal components.
Securing the position of the input shaft is the Active Bevel Gear Flange Nut (Parte não. 2402069-A0E). This is not a standard fastener; it is a calibration point for the entire Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW conjunto. Proper torque application on this nut sets the initial preload for the system. If this nut loosens due to chassis vibration, the active gear will shift axially, destroying the contact pattern and leading to catastrophic failure within kilometers of operation.
The structural alignment is further reinforced by the Hexagon Head Pilot Bolt (Parte não. CQ1500812S). These pilots ensure that the mating flanges are perfectly centered before the main torque bolts are tightened. This attention to assembly logic allows the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW to maintain concentricity even under the twisting loads of off-road articulation, preserving the longevity of the spline connections and reducing vibration transmission to the driver’s cabin.
Bearing Architecture and Thermal Management
The rotational stability of the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW is dependent on a robust bearing configuration. The assembly utilizes a Tapered Roller Bearing (Parte não. 32314) at the front and a larger Tapered Roller Bearing (Parte não. 32315) na parte traseira. This back-to-back arrangement is engineered to handle the massive thrust loads generated by the spiral bevel design, preventing the gear from ejecting itself from the housing under load.
Spacing is critical in this thermal environment. The Spacer – Active Bevel Gear Bearing (Parte não. 2502088-A0E) defines the distance between the bearing races. No Ártico, the steel housing of the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW contracts significantly. This spacer is manufactured from a material with a specific thermal expansion coefficient to match the housing, ensuring that the bearing preload remains constant whether the truck is cold-starting or running at peak heat.
Fine-tuning is achieved via the Adjusting Washer – Active Bevel Gear Bearing (Parte não. 2402081-A0E). Technicians use these washers to set the pinion depth to micron-level accuracy. Correct pinion depth ensures that the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW engages the crown wheel at the strongest point of the tooth flank. Incorrect adjustment leads to noise and rapid wear, making these washers indispensable for rebuilding differentials in remote workshops.
The entire rotating assembly is supported by the Bearing Seat (Parte não. 2502049-A6E). This casting is robust enough to absorb the radial shock loads when the wheels impact frozen ruts. The interface between the bearing seat and the main housing is sealed to prevent oil bypass, garantindo que o Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW bearings receive a continuous flow of lubricant, which is vital when using high-viscosity winter gear oils.
Pneumatic Differential Lock Logic
Traction control is the defining feature of the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW sistema. The inter-wheel differential lock allows the truck to navigate ice by mechanically linking the axle shafts. This function is powered by the Cylinder – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Parte não. 2406011-A0E), which receives compressed air from the vehicle’s auxiliary circuit. The cylinder wall is honed to reduce friction, ensuring a rapid response time when the driver toggles the switch.
Inside the cylinder, the Piston – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Parte não. 2406013-A0E) translates air pressure into mechanical force. The sealing integrity of this piston is paramount for the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW funcionalidade. A failed seal means no lock engagement. Portanto, the system uses a specialized O-ring – Differential Lock Piston (Parte não. 2406014-55R) formulated from low-temperature elastomers that remain flexible down to -50°C, preventing air leaks common in standard rubber seals.
The force from the piston moves the Shift Fork – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Parte não. 2406024-A0E). This fork slides the locking collar over the splines, creating a solid connection. The durability of the fork tips is increased in the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW specification to resist wear from repeated engagement. A worn fork can lead to incomplete locking, causing the collar to jump teeth and damage the axle shafts permanently.
Safety is ensured by the Return Spring – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Parte não. 2406028-A0E). Once the air pressure is released, this heavy-duty spring forces the piston back, disengaging the lock. Immediate disengagement is crucial for the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW sistema; if the lock remains engaged on high-traction surfaces like dry pavement, the driveline will bind up during turns, potentially shearing the axle shafts or exploding the differential case.
Housing Integrity and Fastening Systems
The backbone of the assembly is the Reducer Shell (Parte não. 2502015-A6E). Cast from a specific nodular iron alloy, this shell provides the rigid framework required to maintain gear alignment under load. A metalurgia do Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW housing is selected for its impact resistance at low temperatures. Standard cast iron becomes brittle in the Arctic, but this shell is designed to absorb the kinetic energy of suspension impacts without cracking.
Securing the housing components requires high-tensile fasteners. O parafuso – Fastening Reducer (Parte não. 2402016-1H) is a flange bolt engineered to maintain clamping force under severe vibration. No Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW conjunto, these bolts are torqued to yield, ensuring that the flange faces are friction-welded together. This prevents the reducer from shifting on the axle housing, which would misalign the driveshaft and cause vibration.
Maintenance access is provided via the Hexagon Cone Magnetic Plug (Parte não. T62106). This plug serves a dual purpose: draining the oil and monitoring internal wear. The magnet captures ferrous particles generated by the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW. During service, an excessive accumulation of metal shavings on this plug warns the technician of abnormal gear or bearing wear, allowing for preventative repairs before a total system failure occurs on the road.
Finalmente, the torsional loads are managed by the Supporting Pin (Parte não. 2402021-A0E). These pins act as shear anchors between the reducer shell and the axle housing. Quando o Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW transmits thousands of Newton-meters of torque, the housing tries to rotate. The supporting pins absorb this rotational force, protecting the mounting bolts from shear stress and ensuring the structural integrity of the entire middle axle assembly.
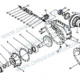
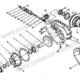
Divisão de Componentes: 137. Reducer Shell & Active Bevel Gear Assembly
| Não. |
Número da peça |
Nome da peça |
Quantidade |
| – | 2502010-55R | Middle Axle Main Reducer Assembly (i=1.500) | 1 |
| 1 | 2402069-A0E | Noz – Flange de engrenagem cônica ativa | 1 |
| 2 | 2502108-A6E | Equipamento cilíndrico acionado | 1 |
| 3 | 32314 | Rolamento de rolo cônico | 1 |
| 4 | 2402081-A0E | Ajuste da arruela – Active Bevel Gear Bearing | 1 |
| 5 | 2502088-A0E | Espaçador – Active Bevel Gear Bearing | 1 |
| 6 | 2402016-1H | Parafuso – Fastening Reducer | 12 |
| 7 | 2502049-A6E | Bearing Seat | 1 |
| 8 | 2502097-A6E | Ajustando calço – Active Bevel Gear Bearing Seat | Conforme necessário |
| 9 | 2402048-A0E | Oil Shield – Active Bevel Gear Bearing Seat | 1 |
| 10 | 32315 | Rolamento de rolo cônico | 1 |
| 11 | 2502036BA6E | Active Bevel Gear | 1 |
| 12 | T62106 | Hexagon Cone Magnetic Plug | 1 |
| 13 | 2402017-1H | Parafuso – Fastening Reducer | 18 |
| 14 | 2403071-A0E | Anel de ajuste – Rolamento diferencial | 2 |
| 15 | 2503010BA6E | Montagem Diferencial | 1 |
| 16 | 2403072-A0E | Placa de bloqueio – Anel de ajuste | 2 |
| 17 | CQ1500812S | Parafuso piloto de cabeça hexagonal | 2 |
| 18 | 2402023-A0E | Parafuso – Fastening Differential Bearing Cap | 4 |
| 19 | 2402021-A0E | Supporting Pin – Reducer Shell & Habitação do eixo | 2 |
| 20 | 2406034-A0E | Steel Wire Retaining Ring – Diff Lock Sleeve | 1 |
| 21 | 2406033-A0E | Fixed Sleeve – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 22 | 2406032-A0E | Moving Sleeve – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 23 | 2402016-A0E | Parafuso – Fastening Reducer | 2 |
| 24 | 2406028-A0E | Spring de retorno – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 25 | 2406024-A0E | Shift Fork – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 26 | 2406025-A0E | Shift Fork Shaft Assembly | 1 |
| 27 | 2406014-55R | Anel-O – Differential Lock Piston | 1 |
| 28 | 2406013-A0E | Pistão – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 29 | 2406011-A0E | Cilindro – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 30 | 2406017-A0E | Junta – Cylinder Cover | 1 |
| 31 | 2406016-A0E | Cobrir – Cilindro | 1 |
| 32 | 2406018-A0E | Parafuso – Fastening Inter-wheel Diff Lock Cylinder Cover | 3 |
| 33 | CQ63505 | Elbow Fitting – Tapered Pipe Joint | 1 |
| 34 | 3834050-A0E | Inter-wheel Differential Lock Switch Assembly | 1 |
| 35 | 2502015-A6E | Reducer Shell & Differential Bearing Cap Assembly | 1 |
| 35-1 | 2502018-A6E | Reducer Shell – Eixo Médio | 1 |
| 35-2 | 2402019-A0E | Boné – Rolamento diferencial | 1 |
| 35-3 | 2502019-A0E | Boné – Rolamento diferencial | 1 |
Conclusão: Maintenance for Longevity
O Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW assembly is the strategic fulcrum of the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z driveline, balancing engine power with the delicate requirements of traction control on icy substrates. By integrating a robust reducer shell with a precision-machined gear set and a fail-safe pneumatic locking system, FAW has created a component that thrives where others freeze. Regular inspection of the magnetic plug and ensuring the air supply is dry are critical for maximizing the lifespan of this sophisticated system.
Investing in genuine replacement parts for the Engrenagem cônica ativa russa FAW system ensures that the vehicle retains its original factory specifications for torque handling and cold-weather resilience. Cada parafuso, from the small pilot bolts to the large reducer fastening bolts, plays a role in maintaining the structural rigidity required for heavy haulage. In the unforgiving landscape of the Russian North, this attention to detail transforms a standard dump truck into an unstoppable logistical asset, capable of delivering uptime regardless of the thermometer reading.
Embalagem e Logística
Peças FAW, incluindo o conjunto do bloco de cilindros, são embalados com cuidado para garantir uma entrega segura. Cada componente é protegido por materiais de proteção para evitar danos durante o transporte. A rede logística garante envios pontuais em todo o mundo, apoiando operações de manutenção eficientes. Abaixo está uma imagem ilustrando a embalagem padrão para peças de caminhão FAW, mostrando a atenção aos detalhes no manuseio e armazenamento.
Esta abordagem de embalagem minimiza o risco de corrosão ou danos por impacto, garantindo que peças como o conjunto do bloco de cilindros FAW cheguem em perfeitas condições. Os clientes podem confiar na logística da FAW para obter qualidade e confiabilidade consistentes.