Lógica del sensor del eje delantero ruso FAW: Sincronizando 4 Unidades de precisión para una estabilidad de dirección absoluta
El Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW El conjunto lógico es el punto principal de adquisición de datos para el sistema de frenos antibloqueo. (abdominales) en el eje de dirección del camión volquete CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z. En las peligrosas condiciones de conducción del Ártico ruso, donde el control de la dirección a menudo se ve comprometido por el hielo negro, el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW Proporciona los datos de velocidad de las ruedas con una precisión de milisegundos necesarios para evitar bloqueos.. Esta guía detalla el bracketry especializado, tecnología de sensores, y protección del cableado que componen el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW asamblea, Garantizar que se mantenga la autoridad direccional incluso durante paradas de pánico a -50 °C..
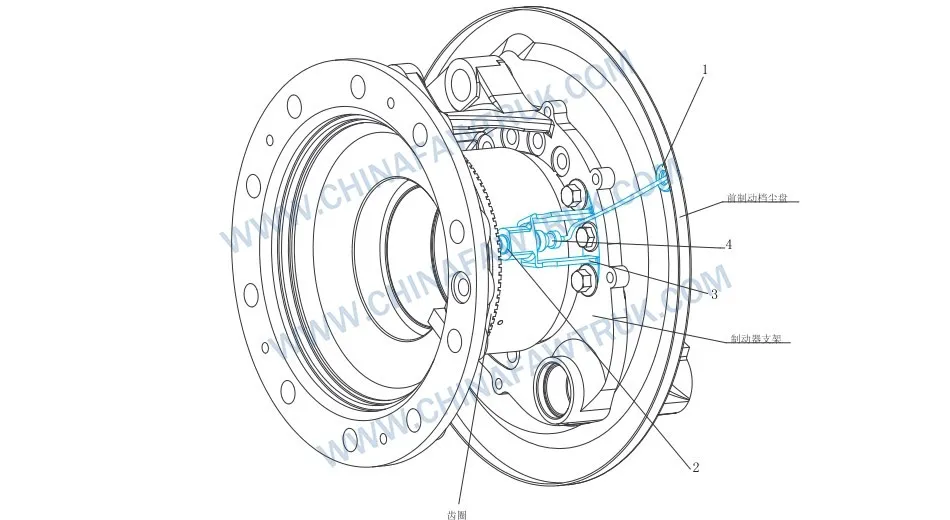
Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW
| No. |
Número de pieza |
Nombre de la pieza |
Cantidad |
| 1 | 3550221-6S | Buje del cable del sensor de velocidad de la rueda | 1 |
| 2 | 3550361-6S | Manga del sensor | 1 |
| 3 | 3605215-820 | Conjunto de soporte del sensor de velocidad de la rueda | 1 |
| 4 | 3605360-820 | Conjunto del sensor de velocidad de la rueda | 1 |
Tecnología de sensores: El ojo del ABS
La piedra angular de la Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW la lógica es la Conjunto del sensor de velocidad de la rueda (Número de pieza. 3605360-820). Este sensor inductivo tiene la tarea de monitorear la rotación de las ruedas delanteras., cuáles son los más críticos para la estabilidad direccional. A diferencia de los sensores traseros que simplemente gestionan la tracción, el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW debe proporcionar datos que permitan a la ECU diferenciar entre un derrape y una acción de dirección. El cabezal del sensor contiene una bobina enrollada alrededor de un imán permanente., encerrado en una carcasa de acero inoxidable para resistir el impacto de la grava arrojada por los neumáticos.
La señal de voltaje generada por el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW es una onda sinusoidal analógica creada por los dientes que pasan de la rueda polar (anillo de tono). En el contexto específico del mercado ruso, El circuito interno del sensor está reforzado para manejar “remojo en frio” condiciones. Los sensores estándar pueden sufrir circuitos abiertos internos cuando el compuesto de encapsulado se contrae a -45 °C., cortando los finos alambres de cobre. El Conjunto del sensor de velocidad de la rueda utilizado en el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW El kit utiliza un epoxi de baja expansión y cables internos flexibles para garantizar que se mantenga la continuidad independientemente de la temperatura ambiente..
La claridad de la señal es otra prioridad para el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW. El eje delantero está ubicado cerca del alternador y de los cables de arranque de alta corriente., fuentes de interferencias electromagnéticas significativas (EMI). El cable del sensor cuenta con un blindaje trenzado y cableado de par trenzado para rechazar este ruido.. si el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW la señal fue corrompida por EMI, El ABS podría dispararse falsamente durante el frenado normal., Ampliar las distancias de frenado en lugar de acortarlas.. Esta señal de alta fidelidad garantiza que el camión se detenga de forma segura y predecible en las superficies variables de un camino de acarreo minero..
Arquitectura de montaje: El conjunto del soporte
La estabilidad física del Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW está asegurado por el Conjunto de soporte del sensor de velocidad de la rueda (Número de pieza. 3605215-820). Esta no es una simple pieza estampada.; Es un componente mecanizado con precisión diseñado para alinear perfectamente la punta del sensor con el anillo fónico dentro del cubo de la rueda.. El eje delantero sufre importantes cargas de impacto cuando el camión choca contra baches y surcos.. El soporte debe ser lo suficientemente rígido para evitar que Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW de vibrar, lo que modularía el entrehierro y crearía un “Fantasma” señal de velocidad.
La ubicación de montaje del Conjunto de soporte del sensor de velocidad de la rueda en el muñón de dirección presenta un desafío único: El cable debe adaptarse al ángulo de dirección.. Mientras la rueda gira de un tope a otro, la distancia entre el sensor y el arnés del chasis cambia. El diseño del soporte incluye guías de enrutamiento específicas para garantizar que el cable se enrolle correctamente sin engancharse en la cámara de freno o los brazos de suspensión.. Esta gestión dinámica de cables es una característica clave del Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW lógica, Proteger el cableado contra fallas por fatiga..
La resistencia a la corrosión también está incorporada en el Conjunto de soporte del sensor de velocidad de la rueda. Expuesto al rocío de productos químicos descongelantes., un soporte de acero estándar se oxidaría e hincharía, potencialmente aplastar el cuerpo del sensor. El Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW El soporte está tratado con un revestimiento de escamas de zinc o galvanización de alta resistencia.. Esto garantiza que el sensor se pueda retirar durante años de servicio en el futuro.. Un sensor atascado a menudo provoca la destrucción del soporte durante el desmontaje., por lo que esta protección contra la corrosión reduce directamente los costos de mantenimiento a largo plazo del Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW sistema.
La interfaz: Lógica de manguito y buje
La interfaz entre el soporte estático y el sensor ajustable es gestionada por el Manga del sensor (Número de pieza. 3550361-6S). Este componente es el héroe anónimo de la Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW asamblea. Crea un ajuste de fricción que mantiene el sensor en su lugar contra la vibración de la carretera pero permite empujarlo hacia atrás si el descentramiento del cojinete de la rueda hace que el anillo tonificador golpee la punta del sensor.. Este “empujar hacia atrás” La capacidad es un mecanismo crítico de autoconservación para el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW, Evitar que el cabezal del sensor se corte durante eventos extremos de articulación de la suspensión..
El material del Manga del sensor Es una aleación de cobre o acero inoxidable para resortes de alta memoria.. En el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW especificación, este material debe conservar su elasticidad a temperaturas bajo cero. Si la funda pierde su agarre con el frío, el sensor saldrá del orificio, aumentando el espacio de aire. Un entrehierro excesivo debilita la señal de voltaje., provocando que la luz ABS se encienda y desactivando el sistema de seguridad. Por lo tanto, la fuerza de sujeción del Manga del sensor es un parámetro vital para la confiabilidad del Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW.
La protección del cable se ve reforzada aún más por el Buje del cable del sensor de velocidad de la rueda (Número de pieza. 3550221-6S). Esta arandela de goma asegura el cable cuando sale del entorno hostil del extremo de la rueda y entra en el riel protegido del chasis.. En el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW diseño, Este casquillo evita que el aislamiento del cable roce con los bordes afilados de los soportes metálicos.. Hecho de caucho EPDM, sigue siendo flexible en el invierno ruso, asegurando un sello hermético alrededor del cable y evitando que la humedad entre al arnés.
Mejores prácticas de diagnóstico y reemplazo
Diagnóstico de problemas con el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW Generalmente se trata de un multímetro y un osciloscopio.. La resistencia a través de los pines del sensor normalmente debería caer entre 1100 y 1800 ohmios. Sin embargo, una prueba de resistencia de aislamiento es igualmente importante para el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW; La verificación de cortocircuitos a tierra puede revelar si los devanados internos han tocado la carcasa debido a daños por expansión térmica.. Al girar la rueda con la mano, el sensor debe generar al menos 0,2 V CA; si no es así, el entrehierro gestionado por el Manga del sensor es probable que sea demasiado grande.
Al reemplazar el Conjunto del sensor de velocidad de la rueda, es obligatorio reemplazar el Manga del sensor (Número de pieza. 3550361-6S) simultáneamente. Reutilizar una funda vieja en el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW la configuración invita al fracaso, ya que la memoria metálica está fatigada y no sujetará el nuevo sensor de forma segura. El agujero en el Conjunto de soporte del sensor de velocidad de la rueda Debe limpiarse de todo óxido y grasa vieja con un cepillo de alambre.. La aplicación de una grasa dieléctrica especializada al cuerpo del sensor puede ayudar a prevenir futuras convulsiones., pero se debe evitar el antiagarrotamiento estándar si contiene partículas metálicas conductoras que podrían interferir con el flujo magnético..
Finalmente, el recorrido del cable a través del Buje del cable del sensor de velocidad de la rueda Se debe verificar que la holgura sea adecuada.. La dirección debe girarse completamente hacia la izquierda y hacia la derecha para garantizar que el cable no quede tenso.. El Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW es tan fiable como su conexión al camión. Asegurándose de que el cable esté libre de tensiones y que el sensor esté asentado de forma segura en una funda nueva, Los equipos de mantenimiento pueden garantizar la seguridad activa del vehículo en las condiciones de conducción más difíciles..
Conclusión: Dirigir con confianza
El Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW El conjunto lógico es un sistema compacto con un impacto enorme en la seguridad del vehículo.. Al convertir la rotación de la rueda en datos digitales, Permite que el camión mantenga el control de la dirección durante el frenado de emergencia sobre hielo.. El 4 componentes: el sensor, soporte, manga, y casquillo: forman una unidad cohesiva diseñada para sobrevivir a los rigores del entorno ruso.
Para operadores de flotas, el Sensor de eje delantero ruso FAW es un elemento de seguridad no negociable. El uso de piezas originales garantiza que las características de la señal coincidan con las expectativas de la ECU, evitando la activación falsa del ABS. Manteniendo estos sensores y su hardware de montaje, Las flotas garantizan que sus conductores tengan la tecnología que necesitan para navegar de forma segura., protegiendo tanto al personal como a la valiosa maquinaria a su cargo.
Embalaje y Logística
piezas FAW, incluido el conjunto del bloque de cilindros, Se empaquetan con cuidado para garantizar una entrega segura.. Cada componente está asegurado con materiales protectores para evitar daños durante el transporte.. La red logística garantiza envíos puntuales en todo el mundo., apoyando operaciones de mantenimiento eficientes. A continuación se muestra una imagen que ilustra el embalaje estándar de las piezas de camiones FAW., mostrando la atención al detalle en el manejo y almacenamiento.
Este enfoque de embalaje minimiza el riesgo de corrosión o daños por impacto., asegurando que piezas como el conjunto de bloque de cilindros FAW lleguen en perfectas condiciones. Los clientes pueden confiar en la logística de FAW para obtener calidad y confiabilidad constantes.