

Welcome to this critical technical breakdown of the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab (Lower Mounts). This system is the structural foundation for the cab-over-engine suspension on the FAW Jiefang CA4251P66K24T1A3E5 6×4 diesel semi-trailer tractor. This is not a single part, but a “logic” assembly of heavy-duty brackets and specialized, high-tensile fasteners. Its core “logic” is to provide the lower anchor point for the cab’s main shock absorbers and springs (both coil and air), isolating the driver from the severe vibration and shock of the chassis.
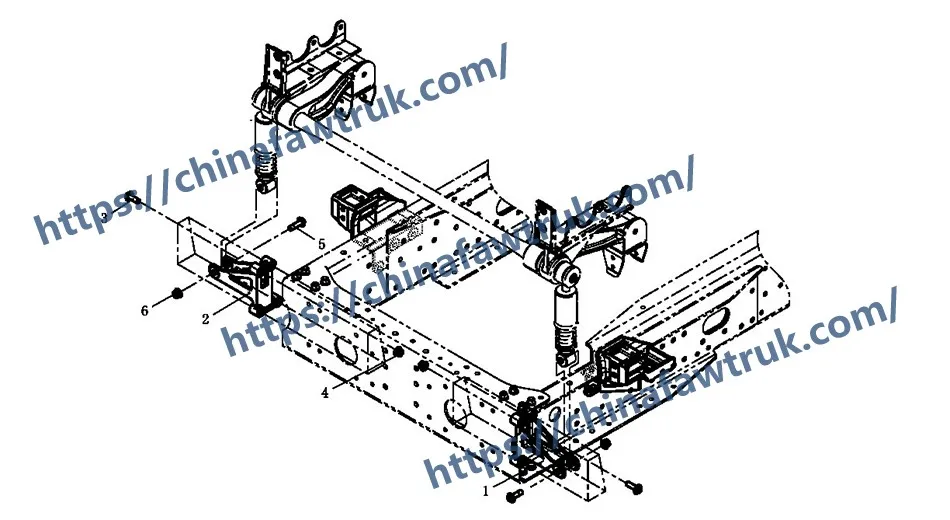
The FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab is the critical interface between the chassis frame and the cab’s vibration-damping system. The components detailed here are designed for universality, supporting both coil spring and air spring front suspension setups. A secure, geometrically perfect front suspension is essential for driver comfort, control, and the prevention of long-term fatigue on both the driver and the cab structure itself.
This in-depth guide is an essential resource for chassis technicians, alignment specialists, and parts managers. We will deconstruct the entire FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab into its 6 primary component types. We will analyze the “Left” and “Right” structural brackets as the main MSUs, and, just as importantly, deconstruct the two different sets of high-tensile, vibration-proof fasteners, each with its own specific “logic.”
This section is the “longer” and most substantial part of the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab. The primary components are the two main “large purchase” MSUs:
These two components are the bedrock of the front cab suspension. Their “logic” is to serve as the structural anchor point, transferring the entire static and dynamic load of the cab’s front end from the shock absorber and spring into the truck’s main chassis frame.
Construction and Logic:
These brackets are not simple cast iron parts. They are high-strength, fabricated steel assemblies. This “logic” of using fabricated (welded) heavy-gauge plate steel is for superior fatigue resistance. A cab suspension is subjected to millions of micro-vibrations and high-impact shocks (from potholes) during its lifespan. A cast part could become brittle and crack; this fabricated design provides the necessary ductility and strength to survive.
As the ‘Left’ and ‘Right’ designations imply, these are mirror-image components. Their geometry is critical. The location of the main mounting holes (for attaching to the frame) and the shock absorber mounting holes are precision-drilled. If one of these brackets is bent or damaged in a collision, the cab will sit “crooked” on the chassis, leading to alignment issues, driver discomfort, and uneven stress on the other suspension components.
Serviceability (MSU):
These brackets are primary MSUs. Failure is rare, but if it occurs (typically from collision damage or a fatigue crack in a weld), the entire bracket is replaced. It is secured to the chassis frame by the 8-bolt fastener set (MSUs 3 & 4) and serves as the mounting point for the shock absorber via the 2-bolt fastener set (MSUs 5 & 6). A key part of the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab, its integrity is paramount.
This group represents the first, and most numerous, set of fasteners in the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab. It consists of eight (8) ‘Hexagon flange bolts’ (01841470T) and eight (8) ‘Hexagon head self-locking nuts’ (Q032614).
The “logic” of this 8-bolt/8-nut system is clear: this is the high-strength hardware used to mount the two brackets (MSUs 1 & 2) *to the main chassis frame*. This implies a secure, four-bolt pattern for each of the two brackets.
Bolt (01841470T): This is a ‘Hexagon flange bolt’. The “flange” logic is critical. The flange is a built-in, non-rotating, integrated washer. This design distributes the clamping force of the bolt head over a wider surface area, preventing the bolt from “sinking” into the bracket’s mounting holes. It also makes assembly faster, as the technician does not need to fumble with a separate washer.
Nut (Q032614): This is a ‘Hexagon head self-locking nut’. This is the most important “logic” in the entire assembly. This is a “Nyloc” (nylon-insert) or “prevailing torque” nut. The nylon insert creates intense friction on the bolt threads, which *prevents the nut from backing off due to vibration*. On a component as critical as the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab, a standard nut would vibrate loose in days. This self-locking logic is a non-negotiable safety feature.
Serviceability (MSU): This entire set of 16 fasteners are MSUs. Critically, self-locking nuts are *single-use items*. Once a Q032614 nut is removed, the nylon insert is compromised and it *must not* be re-used. A new self-locking nut must be used to guarantee the anti-vibration logic.
This second, smaller set of fasteners is functionally different from the first. It consists of two (2) ‘Hexagon flange bolts’ (T18414100T) and two (2) ‘Hexagon flange nuts’ (Q39614).
The “logic” of this 2-bolt/2-nut system (one per side) indicates it is the hardware used to attach the *bottom of the shock absorber* (or air spring) *to the bracket*.
Bolt (T18414100T): The part name, ‘Hexagon flange bolt, tapered guide end’, tells the whole story. The “tapered guide end” is the critical “logic” here. This bolt is specifically designed to aid in assembly. The tapered point acts as an alignment dowel, allowing the technician to easily guide the bolt through the bracket hole and the heavy, hard-to-move “eye” of the shock absorber. This “alignment logic” saves significant time and frustration during service.
Nut (Q39614): This is a ‘Hexagon flange nut’. Like the other bolts, the flange acts as an integrated washer. This nut is torqued to a high specification against the bolt to create the clamping force necessary to hold the shock absorber in place, allowing the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab to properly absorb and dampen road forces.
The following table provides the complete, detailed breakdown of all 6 component types identified in the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab (Lower) diagram for the FAW CA4251P66K24T1A3E5 tractor.
| Mark | Part No. | Part Name | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5001161A91W | Front suspension shock absorber left lower bracket | 1 |
| 2 | 5001162A91W | Front suspension shock absorber right lower bracket | 1 |
| 3 | 01841470T | Hexagon flange bolt (coarse thread) (standard type) | 8 |
| 4 | Q032614 | Hexagon head self-locking nut | 8 |
| 5 | T18414100T | Hexagon flange bolt, tapered guide end | 2 |
| 6 | Q39614 | Hexagon flange nut | 2 |
The specifications for the FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab are defined by its function as the primary structural mounting point for the cab’s damping system. It is engineered for high strength and vibration resistance.
| Vehicle Application | FAW Jiefang CA4251P66K24T1A3E5 6×4 Tractor |
| Component Group | FAW Front Suspension Assembly For The Cab (Lower) |
| Suspension Type | Universal (Coil Spring / Air Spring compatible) |
| MSU 1 (Left Bracket) | 5001161A91W |
| MSU 2 (Right Bracket) | 5001162A91W |
| MSUs 3 & 4 (Bracket-to-Frame) | 8x Flange Bolt (01841470T) + 8x Self-Locking Nut (Q032614) |
| MSUs 5 & 6 (Damper-to-Bracket) | 2x Tapered Flange Bolt (T18414100T) + 2x Flange Nut (Q39614) |
| Bracket Material | Fabricated High-Strength Steel |
| Fastener Logic | Flange (Anti-Washer), Self-Locking (Anti-Vibration), Taper (Alignment) |
FAW parts, including the Cylinder Block Assembly, are packaged with care to ensure safe delivery. Each component is secured in protective materials to prevent damage during transit. The logistics network guarantees timely shipments worldwide, supporting efficient maintenance operations. Below is an image illustrating the standard packaging for FAW truck parts, showcasing the attention to detail in handling and storage.

This packaging approach minimizes the risk of corrosion or impact damage, ensuring that parts like the FAW Cylinder Block Assembly arrive in perfect condition. Customers can rely on FAW’s logistics for consistent quality and reliability.