Lógica de bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW: 35 Componentes estratégicos para una tracción ártica imparable
El Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW logic assembly is the definitive traction management solution for the heavy-duty CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z dump truck. Engineered to navigate the treacherous ice roads of the Siberian mining sector, this pneumatic-mechanical system ensures that torque is delivered equally to both wheels when traction is compromised. By overriding the standard differential action, this assembly transforms the axle into a solid spool, providing the grip necessary to climb frozen gradients at -50°C. This technical guide breaks down the critical interplay between the pneumatic cylinder, the mechanical shift fork, and the sliding sleeves.

Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW
Pneumatic Actuation in Extreme Cold
The activation sequence of the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW begins with the pneumatic system. Unlike hydraulic locks that can become sluggish as fluids thicken in the cold, this system relies on compressed air delivered through the Elbow Fitting – Junta de tubería cónica (Número de pieza. CQ63505). This fitting channels high-pressure air directly into the Cylinder – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Número de pieza. 2406011-A0E). The internal geometry of this cylinder is honed to a mirror finish to minimize friction, ensuring that the Piston – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Número de pieza. 2406013-A0E) can travel smoothly even when the ambient temperature drops well below freezing.
The critical failure point in most arctic pneumatic systems is the seal. El Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW addresses this by utilizing a specialized O-ring – Pistón de bloqueo del diferencial (Número de pieza. 2406014-55R). El “55R” suffix indicates a low-temperature elastomer formulation. Standard rubber O-rings harden and shrink in extreme cold, creating air leaks that render the lock useless. This specialized component retains its elasticity, maintaining a hermetic seal against the cylinder wall. This ensures that when the driver flips the switch, the full force of the air pressure is translated into mechanical motion without loss.
To protect these sensitive internal components from the harsh external environment, the assembly is sealed with the Cover – Cilindro (Número de pieza. 2406016-A0E) and the Gasket – Tapa del cilindro (Número de pieza. 2406017-A0E). This gasket prevents moisture and road brine from entering the cylinder housing. In the Russian winter, any water ingress would immediately freeze, locking the piston in place and potentially causing the differential lock to fail in the engaged position, which is hazardous for highway driving.
The structural integrity of the pneumatic housing is secured by the Bolt – Fastening Inter-wheel Diff Lock Cylinder Cover (Número de pieza. 2406018-A0E). These three bolts must be torqued precisely to compress the gasket evenly without warping the cover. La confiabilidad del Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW depends on this airtight assembly, as even a minor leak can reduce the engagement force, leading to gear slippage and catastrophic damage to the sliding sleeves.
Mechanical Engagement and Torque Transfer
Once the pneumatic piston extends, el Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW transitions to mechanical action. The linear force of the piston pushes the Shift Fork – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Número de pieza. 2406024-A0E). This fork is a heavy-duty casting designed to withstand the resistance of the engagement collar. It rides on the Shift Fork Shaft Assembly (Número de pieza. 2406025-A0E), which provides precise guidance to ensure the fork moves in a perfectly straight line, preventing binding or off-axis loading.
The fork physically moves the Moving Sleeve – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Número de pieza. 2406032-A0E). This sleeve is splined to the axle shaft and slides axially to engage with the Fixed Sleeve – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Número de pieza. 2406033-A0E), which is bolted to the differential case. When these two sleeves mesh, the differential action is physically blocked. The teeth on these sleeves are heat-treated to an extreme hardness to resist “rounding off” if the driver attempts to engage the lock while the wheels are spinning at different speeds—a common operator error in panic situations.
Securing the fixed components is the Steel Wire Retaining Ring – Manguito fijo de bloqueo del diferencial (Número de pieza. 2406034-A0E). This simple yet vital ring ensures that the fixed sleeve cannot back out of its position under the immense torque loads generated when a fully loaded 30-ton truck attempts to climb a grade. El Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW design prioritizes positive retention of all components, as internal looseness would lead to the destruction of the entire differential assembly.
The synchronization of these parts allows the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW to transmit 100% of the available torque to the wheel with traction. In a standard open differential, torque follows the path of least resistance (the spinning wheel on ice). By mechanically linking the axle shafts via these sleeves, the system forces both wheels to turn at the same speed, effectively pulling the vehicle out of deep snow or mud.
Lógica de seguridad: The Return Mechanism
Engaging the lock is critical for traction, but disengaging it is vital for safety. El Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW employs a robust Return Spring – Inter-wheel Differential Lock (Número de pieza. 2406028-A0E). When the driver turns off the switch and air pressure vents from the cylinder, this spring is responsible for pushing the piston and shift fork back to the neutral position. If this spring were to fail due to fatigue or corrosion, the truck would remain locked. Driving a locked vehicle on dry pavement causes “axle wind-up,” which can shear axle shafts or explode the differential carrier.
To prevent such catastrophic failures, the system includes the Inter-wheel Differential Lock Switch Assembly (Número de pieza. 3834050-A0E). This sensor detects the physical position of the locking mechanism and sends a signal to the dashboard. This provides the driver with positive confirmation that the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW is actually engaged or disengaged, rather than just relying on the position of the dashboard toggle. In the noisy, high-vibration environment of a mining truck, this visual feedback is an essential safety feature.
The interplay between the pneumatic force and the spring tension is carefully balanced in the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW diseño. The spring must be strong enough to disengage the lock even if the sliding sleeves are under slight torque load, yet not so strong that the air cylinder cannot overcome it during engagement. This balance ensures rapid response times in both directions, allowing the driver to modulate the system as terrain conditions change rapidly.
Además, the longevity of the return mechanism is supported by clean lubrication. While the locking mechanism shares oil with the main gear set, the movement of the fork and spring must remain free of sludge and metal shavings. The design of the Reducer Shell (Número de pieza. 2502015-A6E) includes internal oil galleys that ensure fresh lubricant reaches the shift fork shaft, preventing the mechanism from seizing due to lack of oil, even when the gear oil is thick and viscous in cold weather.
Assembly Integration and Housing
todo el Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW logic is housed within the Reducer Shell & Conjunto de tapa de cojinete de diferencial (Número de pieza. 2502015-A6E). This large casting is the structural backbone of the middle axle. It must be rigid enough to maintain the alignment of the differential bearings while absorbing the massive reaction forces generated when the lock engages. The Russian-spec housing uses a ductile iron alloy that resists brittle fracture at low temperatures, a common issue with inferior castings in the Arctic.
The assembly is secured to the axle housing using high-tensile Bolt – Reductor de fijación (Número de pieza. 2402016-1h). Estos 12 bolts provide the clamping force necessary to prevent the reducer from shifting under load. Además, the Supporting Pin – Carcasa reductora & Carcasa del eje (Número de pieza. 2402021-A0E) acts as a shear dowel. When the differential lock engages and torque spikes, the housing attempts to rotate; these pins absorb that shear load, protecting the bolts from snapping.
Proper maintenance of the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW involves checking the Hexagon Cone Magnetic Plug (Número de pieza. T62106). Since the sliding sleeves create metal particles as they wear, the magnetic plug traps this debris before it can damage the seal on the locking piston or scour the cylinder walls. Regular inspection of this plug gives fleet managers an early warning of the health of the locking mechanism.
Finalmente, the Cap – Rodamiento diferencial (Número de pieza. 2402019-A0E) secures the differential assembly within the shell. The rigidity of these caps is crucial because if the differential carrier deflects under the load of the lock engagement, the gear teeth will misalign. The robust design of the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW housing ensures that all internal components remain in perfect alignment, guaranteeing reliability season after season.
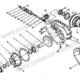
Desglose de componentes: 137. Differential Lock Logic & Reducer Assembly
| No. |
Número de pieza |
Nombre de la pieza |
Cantidad |
| – | 2502010-55R | Conjunto del reductor principal del eje medio (i=1.500) | 1 |
| 1 | 2402069-A0E | Tuerca – Brida de engranaje cónico activo | 1 |
| 2 | 2502108-A6E | Equipo cilíndrico conducido | 1 |
| 3 | 32314 | Rodamiento de rodillos cónicos | 1 |
| 4 | 2402081-A0E | Arandela de ajuste – Rodamiento de engranaje cónico activo | 1 |
| 5 | 2502088-A0E | Espaciador – Rodamiento de engranaje cónico activo | 1 |
| 6 | 2402016-1h | Tornillo – Reductor de fijación | 12 |
| 7 | 2502049-A6E | Asiento del cojinete | 1 |
| 8 | 2502097-A6E | Ajuste de la cuña – Asiento de rodamiento de engranaje cónico activo | Como se requiere |
| 9 | 2402048-A0E | Escudo de aceite – Asiento de rodamiento de engranaje cónico activo | 1 |
| 10 | 32315 | Rodamiento de rodillos cónicos | 1 |
| 11 | 2502036Ba6e | Engranaje cónico activo | 1 |
| 12 | T62106 | Tapón magnético de cono hexagonal | 1 |
| 13 | 2402017-1h | Tornillo – Reductor de fijación | 18 |
| 14 | 2403071-A0E | Anillo de ajuste – Rodamiento diferencial | 2 |
| 15 | 2503010Ba6e | Conjunto diferencial | 1 |
| 16 | 2403072-A0E | Placa de bloqueo – Anillo de ajuste | 2 |
| 17 | CQ1500812S | Perno piloto de cabeza hexagonal | 2 |
| 18 | 2402023-A0E | Tornillo – Fijación de la tapa del cojinete del diferencial | 4 |
| 19 | 2402021-A0E | Pasador de soporte – Carcasa reductora & Carcasa del eje | 2 |
| 20 | 2406034-A0E | Anillo de retención de alambre de acero – Manguito fijo de bloqueo del diferencial | 1 |
| 21 | 2406033-A0E | Manga fija – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 22 | 2406032-A0E | Manga móvil – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 23 | 2402016-A0E | Tornillo – Reductor de fijación | 2 |
| 24 | 2406028-A0E | Resorte de retorno – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 25 | 2406024-A0E | Horquilla de cambio – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 26 | 2406025-A0E | Conjunto del eje de la horquilla de cambio | 1 |
| 27 | 2406014-55R | junta tórica – Pistón de bloqueo del diferencial | 1 |
| 28 | 2406013-A0E | Pistón – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 29 | 2406011-A0E | Cilindro – Inter-wheel Differential Lock | 1 |
| 30 | 2406017-A0E | Empaquetadora – Tapa del cilindro | 1 |
| 31 | 2406016-A0E | Cubrir – Cilindro | 1 |
| 32 | 2406018-A0E | Tornillo – Fastening Inter-wheel Diff Lock Cylinder Cover | 3 |
| 33 | CQ63505 | Ajuste del codo – Junta de tubería cónica | 1 |
| 34 | 3834050-A0E | Inter-wheel Differential Lock Switch Assembly | 1 |
| 35 | 2502015-A6E | Carcasa reductora & Conjunto de tapa de cojinete de diferencial | 1 |
| 35-1 | 2502018-A6E | Carcasa reductora – Eje medio | 1 |
| 35-2 | 2402019-A0E | Tapa – Rodamiento diferencial | 1 |
| 35-3 | 2502019-A0E | Tapa – Rodamiento diferencial | 1 |
Conclusión: Ensuring Traction Security
El Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW is more than just an auxiliary feature; it is the strategic component that ensures mobility in the most unforgiving environments on Earth. From the precise pneumatic metering of the air cylinder to the robust mechanical meshing of the sliding sleeves, every part is engineered to function flawlessly at -50°C. Para operadores de flotas, understanding the maintenance requirements of the cylinder seals, return springs, and air fittings is the key to preventing costly downtime.
By investing in genuine FAW parts for the Bloqueo del diferencial ruso FAW ensamblaje lógico, operators guarantee that their vehicles retain the factory-specified torque handling and safety margins. The capability to lock the axles on demand transforms the CA3250P66K24L1TE5Z from a standard dump truck into an all-terrain logistical powerhouse, capable of delivering results regardless of the ice and snow that define the Siberian operational theater.
Embalaje y Logística
piezas FAW, incluido el conjunto del bloque de cilindros, Se empaquetan con cuidado para garantizar una entrega segura.. Cada componente está asegurado con materiales protectores para evitar daños durante el transporte.. La red logística garantiza envíos puntuales en todo el mundo., apoyando operaciones de mantenimiento eficientes. A continuación se muestra una imagen que ilustra el embalaje estándar de las piezas de camiones FAW., mostrando la atención al detalle en el manejo y almacenamiento.
Este enfoque de embalaje minimiza el riesgo de corrosión o daños por impacto., asegurando que piezas como el conjunto de bloque de cilindros FAW lleguen en perfectas condiciones. Los clientes pueden confiar en la logística de FAW para obtener calidad y confiabilidad constantes.